Learn to extract data from the worldwide popular messaging app Telegram, a must-have social media intelligence (SOCMINT) platform.
Telegram is a free cloud-based internet messaging application first released in 2013. Its cloud-based nature allows Telegram users to synchronize their accounts across different devices, such as mobile phones, tablets and laptops, simultaneously.
Telegram was built on the promise to provide a fast and reliable internet messaging application that users can leverage, similar to phone calls and email. The app allows users to exchange end-to-end encrypted messages and share files of different types up to 2GB in size. It also facilitates group chat and allows up to 200,000 users in each group. Beyond private messaging, messages can be broadcast to an unlimited number of users through public channels.
Telegram is famous for its security features. Not only is communication encrypted, it also has a self-destructing feature to automatically destroy messages from both communication parties. Users can schedule messages to disappear after specific timeframes, ranging from seconds to days. Telegram has many more security and privacy features that can be activated from user accounts, including two-factor authentication and the ability to hide one's phone number.
Practically speaking, businesses use Telegram channels to broadcast product updates and promotions to thousands of followers simultaneously. Journalists in restricted countries leverage its secret chats for confidential communications. Meanwhile, project teams utilize its file-sharing capabilities to exchange large documents without compression.
Telegram has over one billion users worldwide and is considered among the top five most downloaded applications. It is open source, can run on iOS and Android and has dedicated applications for Windows, macOS and Linux desktop operating systems.
| Ensure your digital investigations are truly safe and anonymous with Silo. Try it free for 30 days. |
Inspecting the Telegram user profile
You must provide your phone number to get an account with Telegram which is considered the primary identifier of your account. A Telegram account may have an optional username; this allows a Telegram user to share their account without revealing their phone number.
Inspecting Telegram usernames and display names
The username begins with @ and is case insensitive. When we have someone's Telegram username, we should start by searching for it on other social media platforms. For instance, many users prefer to use the same username across multiple platforms, such as Facebook, Instagram, and X.
Here are some websites to perform a reverse username search:
A Telegram username may have a specific meaning in some civilizations or cultures, so it is helpful to find its meaning. Here are some services that give you the name meaning in different cultures:
To view more details about a target Telegram account, we need to access the profile window:
- Open the Telegram application, in the search bar, type the target username
- Telegram will commonly return a list of accounts, groups and channels that match your search query. We can note from the returned search result in Figure 1 that Telegram identifies a Bot account with an icon. At the same time, channels have another icon and a personal or individual account without an icon.
- Click on the account you want to investigate. Now go and click over their username (see Figure 2) to access the Telegram profile page.
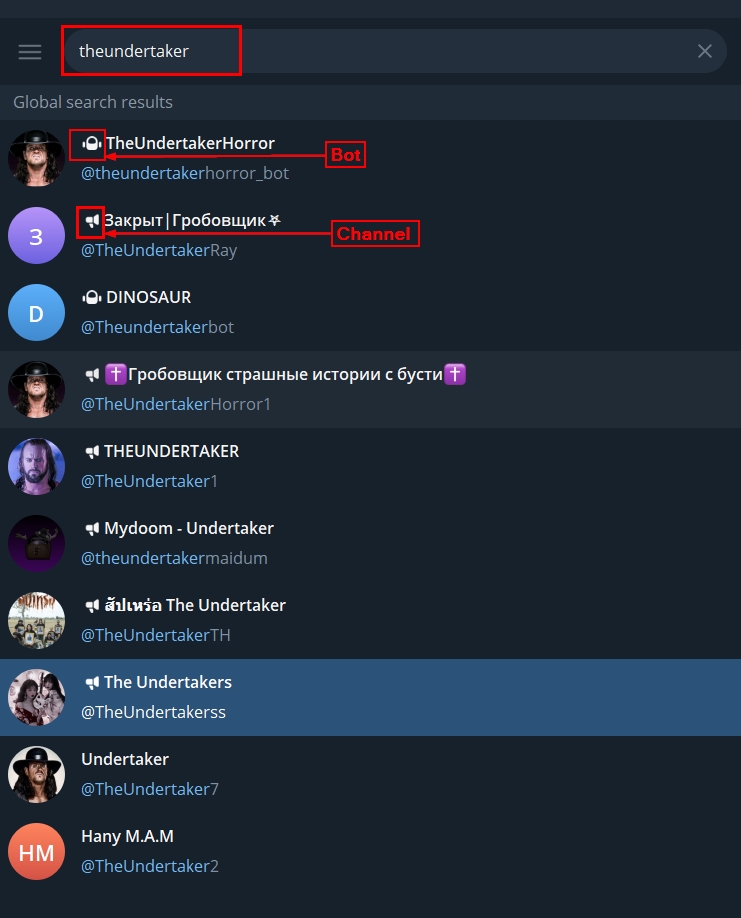
Figure 1 - Search for a Telegram user account
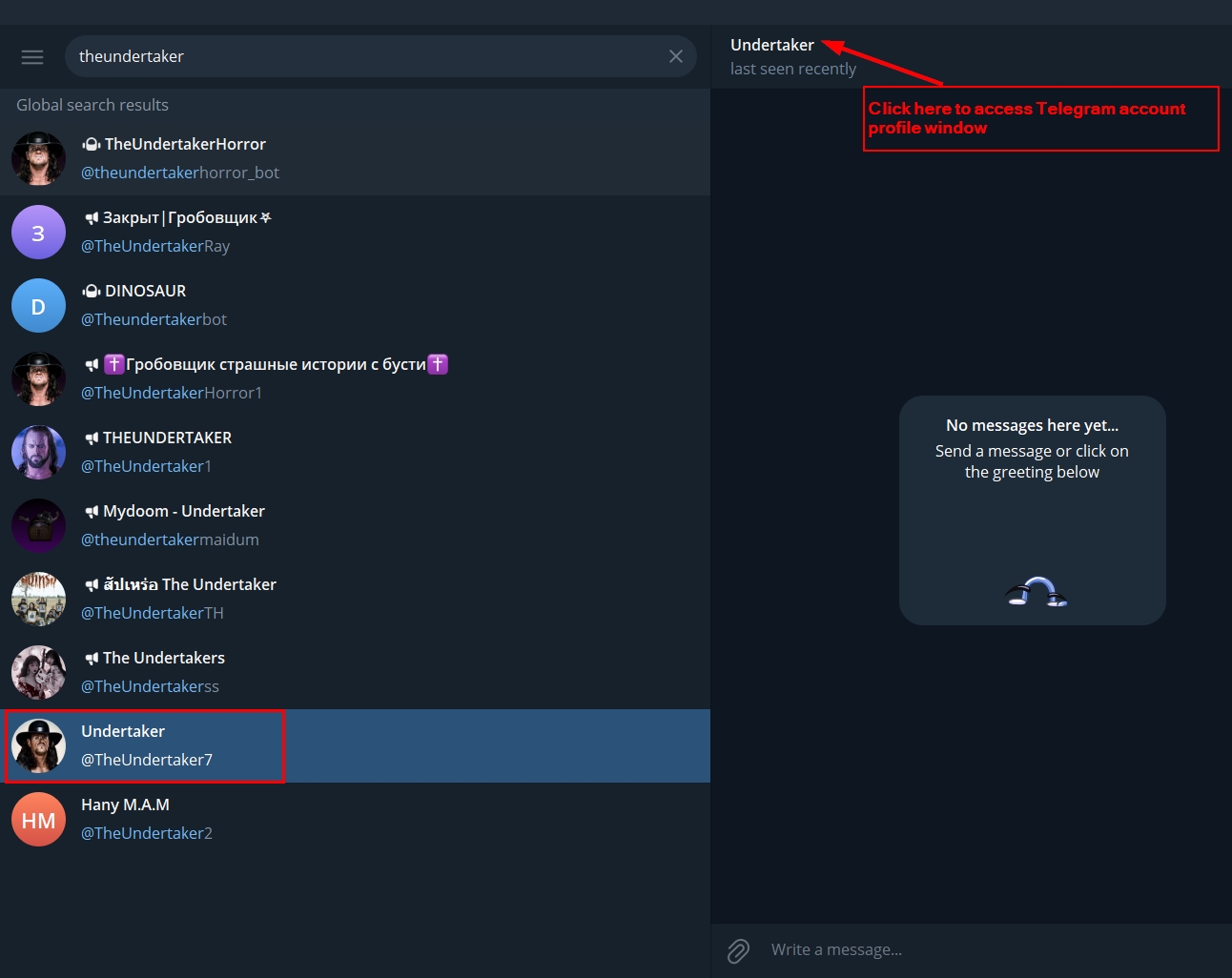
Figure 2 - Access the Telegram user profile page
Telegram allows users to have a "display name". The display name is visible to others in chats and groups. It can be a user's real name, a nickname or any custom text that they choose. The display name is not unique (multiple users can have the same display name across the Telegram platform).
If the Telegram display name points to a user's real name, such as first and last name, then it is worth searching for it across the web to see where it appears. For example, we may discover documents and files containing the display name that can open a new lead for OSINT gatherers. Here are some Google dorks for searching for a Telegram user's "Display name":
- site:linkedin.com "John Doe” (we can change the LinkedIn site to other sites, such as Facebook.com or x.com
- "John Doe" "engineer" (if we know the profession of the target, then we can add it to narrow down returned search results)
- inurl:"john-doe" (search within the URLs of web pages)
- intitle:"John Doe" (search within pages’ titles)
- intext:"John Doe" (search for the display name within the text of web pages)
- (filetype:pdf OR filetype:doc OR filetype:txt OR filetype:rtf OR filetype:odt) "John Doe" (searches for "John Doe" within PDF, DOC, TXT, RTF, and ODT files)
- filetype:doc OR filetype:docx resume "John Doe" (Microsoft Word formats for resumes of "John Doe")
- filetype:pdf resume "John Doe" ("email" OR "phone" OR "contact") (Looks for PDF resumes of "John Doe" that likely include contact details)
Telegram ID
While the Telegram username and display name can be changed, a permanent, unique numerical identifier is created automatically upon account creation and is never changed; this is the Telegram numeric ID. You can get this ID for any Telegram account using tools such as Telepathy and Tosint. There are also Telegram bots that can extract Telegram ID such as this one: @get_user_id_bot (see Figure 3).
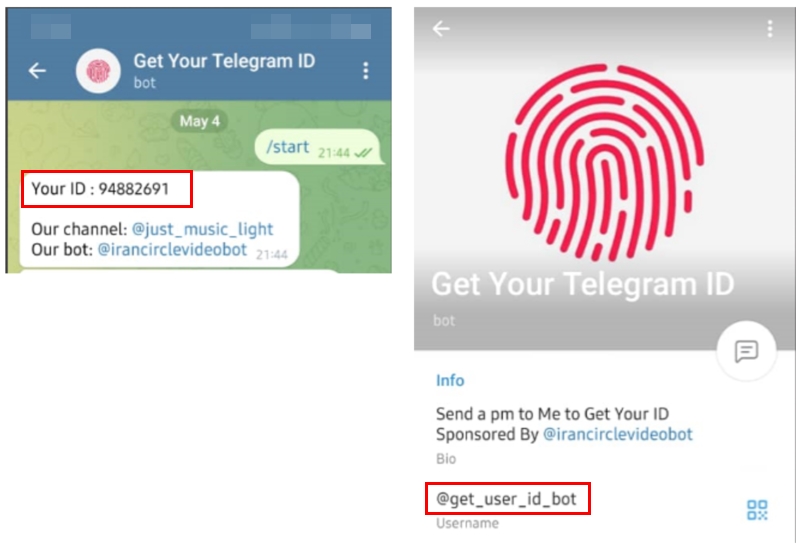
Figure 3 - Fetching a Telegram user numeric ID using a Telegram bot
Inspecting the profile picture
A Telegram account may have a profile picture associated with it. To view the profile image, access the Telegram account and click on the profile image to open it in a large display. Now right-click over it and select “Save As.” (see Figure 4).
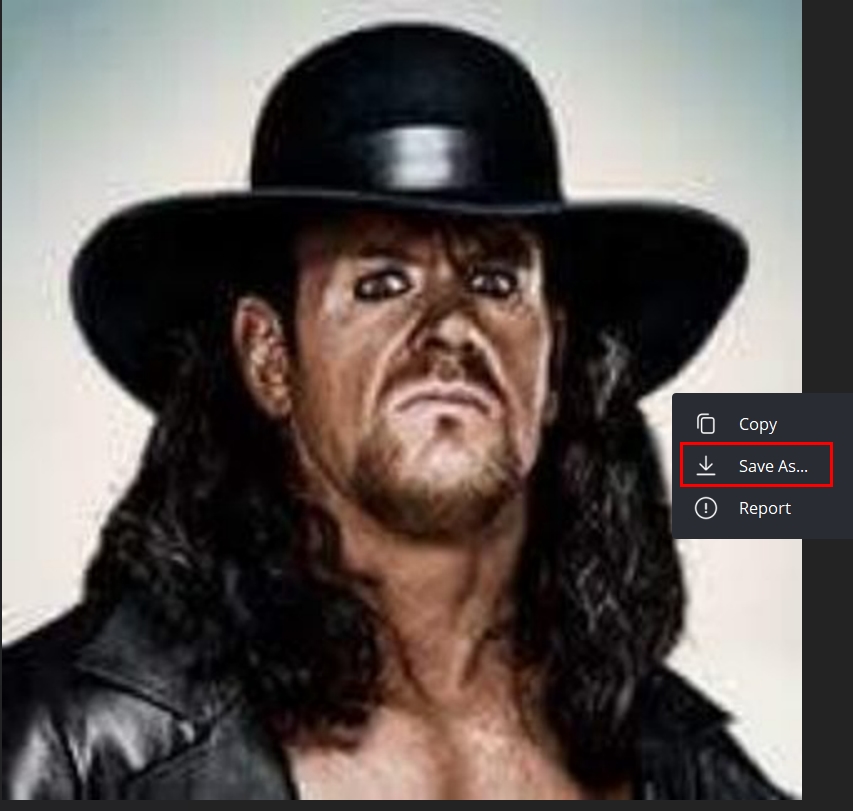
Figure 4 - Open Telegram profile image in full display
After downloading the profile image, we need to execute a reverse image search to see where this image appeared online. This can help us discover linked accounts to target the Telegram profile.
If the profile image contains a personal picture, then we should try searching using the following face search engines:
Inspecting Bio/Description
The Telegram bio may contain important information about the Telegram user that opens new leads for OSINT gatherers, such as:
- Email address
- Political and business affiliation
- Link to other websites, such as a personal blog
- Links to other social media accounts
- Occupational details
If the Bio contains an email address, then we should use services such as:
- Hunter.io – Find email by company or name and verify email addresses.
- Holehe – To check whether an email is attached to an account on sites like X, Instagram, Imgur and more than 120 others.
We should also inspect data breach websites that contain information about breached accounts. This allows us to discover the other online services where this email is used.
Suppose the bio contains usernames on other platforms, such as a username on Instagram, Reddit or LinkedIn. Then we can use a tool like Sherlock to execute a reverse username search for each username.
If the bio contains links to other websites, such as a personal website or blog, then we should inspect it thoroughly (we already wrote a blog about inspecting websites).
Here are some tools for domain intelligence:
- Wayback Machine – To check the historical version of the website. Archived versions may contain important information, such as contact information.
- Domain tools – For Whois lookup, which can reveal registration details and connected entities.
- URLScan – Reveal different technical information about websites and URLs.
Inspect phone number
If the user leaves their phone number visible, this info can provide more information about their location or contacts. Here are some tools/online services for phone search:
- Truecaller – Reverse phone lookup
- Ipqualityscore – Free phone number lookup
- Phone Number Search Tool from aware-online.com
Last Seen status
If enabled by the user, then it will show the last time a user connected to Telegram (e.g., “Last seen recently” or a specific time).
Media shared
We can see shared media content such as text, images, files and videos if the target has posted them to a public group. Inspecting public posts can reveal important information about a user, such as their interests and affiliation, in addition to religious and political thinking.
Public Group/Channel Membership
If the target Telegram user participates in public groups and channels, then their posts (messages) and profile will appear there. OSINT gatherers can search within Telegram groups to find a particular Telegram profile using specialized search engines as we are going to see next. There are also Telegram bots that perform this job for you. @BotoDetective (username: @CALLNAMOBOT) is an example of a bot that allows users to search for information using criteria such as phone number, name, email, social network ID, and more. To use this service, you must authorize the bot to reveal your registered Telegram phone number.
Inspecting Telegram channels and groups
A channel commonly belongs to a business or brand; it can have an unlimited number of subscribers, and only admins can broadcast messages via it.
Telegram groups, on the other hand, are managed by one or more administrators. However, all members can send messages. In that way, it facilitates group discussions and can have up to 200,000 members per group. Groups are created to gather a family, a group of friends or an online community that cares about something, such as nature, technology, arts and entertainment, etc.
A group can be either public: hence, it can be located using its username, or private, where it requires the group owner to add you to it directly or via an invite link. Please note that if you have an invite link to a private group, then you can join it. However, the invite link can be set to expire after a certain time or number of uses.
For practical inspection of channels and groups, follow these steps:
Telegram search engines
Use Telegram's built-in search functionality to find channels and public groups. Enter your search keywords, such as “cybersecurity,” “pirated software” or “cryptocurrencies” to find specific niche groups.
There are also dedicated Telegram search engines that allow you to find even more results than the Telegram built-in search:
- XTEA.io – Search for Telegram groups, channels and bots
- Telemetryapp – Requires registering a free account to use its search feature
- Lyzem – Search for Telegram bots, channels, groups and the text messages within them (see Figure 5)
- Teleteg – Search within the Telegram platform; the free account displays only the first 10 results
- Intelx – A custom Google search engine for Telegram search
- TelegramDB Search Bot - Search hundreds of millions of Telegram chats
- Telegago – Another custom Google search engine for Telegram
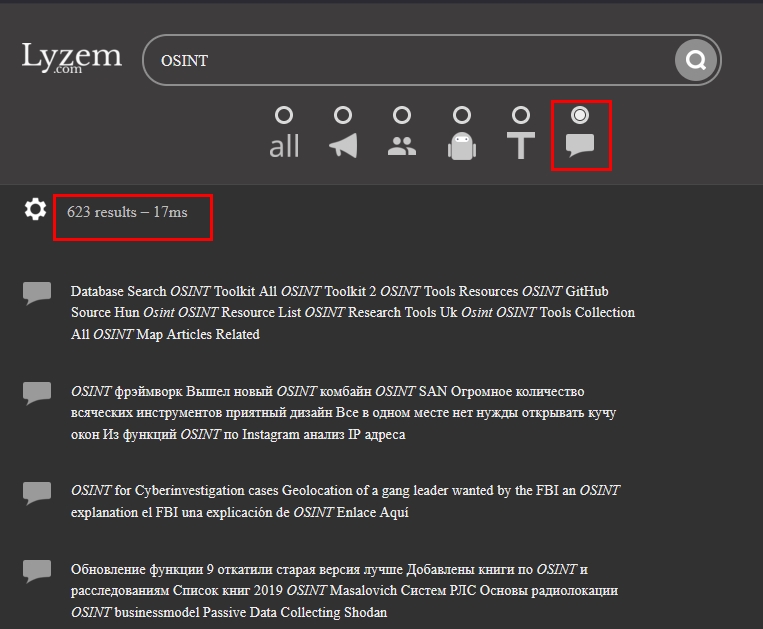
Figure 5 - Lyzem allows searching within groups and channels text messages
Telegram directories and aggregators listing
Telegram directories and aggregators are dedicated services that compile and categorize public Telegram channels, groups and sometimes bots, making it easier to discover communities based on interests, languages or topics. Below is a comprehensive list of Telegram directories and aggregators that list public channels:
- Telegramchannels.me – Contains more than 11,310 Channels, Groups, Bots, and Stickers in English. Users can search using keywords or filter by category.
- Tgstat – A Telegram channel and group catalog
- Tlgrm.eu – A Telegram directory of groups and channels. You can search by name, keywords, or description. It shows different statistical information about each channel/group
- Tdirectory – Search for Telegram channels, groups and bots. For each channel/group, the website displays different analytical information.
- Telega – Telegram channels catalog
- Telegramic – A Telegram directory of bots, channels and groups in addition to stickers
- Telegram-groups – A Telegram groups directory
- Tgdr – Search for Telegram groups, channels and bots
- Telegramguide – A Telegram directory that contains more than 1000 group
- Bestoftelegram – Contains more than 3000 of the best and top Telegram channels, Groups, stickers and bots
Using Google Dorks to find Telegram groups
Google Dorks can also be used to find Telegram groups. Here are some Dorks:
- inurl:t.me/joinchat/ "[keyword]" | Searching for Telegram invite links.
- site:t.me "[keyword]" | Search for public Telegram links.
- intext:"telegram group" OR intext:"telegram channel" "[keyword]" | Search for websites that contains a listing of Telegram links (groups and channels).
- intext:"join telegram group" "[keyword]" | Searching for "Join Telegram Group" phrases. This may reveal links to joining some private communities.
- inurl:(t.me/joinchat | telegram.me/joinchat) | Search for private groups invite links. For example: inurl:t.me/joinchat OSINT finds private group links containing “OSINT” in the page content.
- site:pastebin.com intext:t.me/joinchat | Search in Pastebin website for Telegram private group invites (see Figure 6)
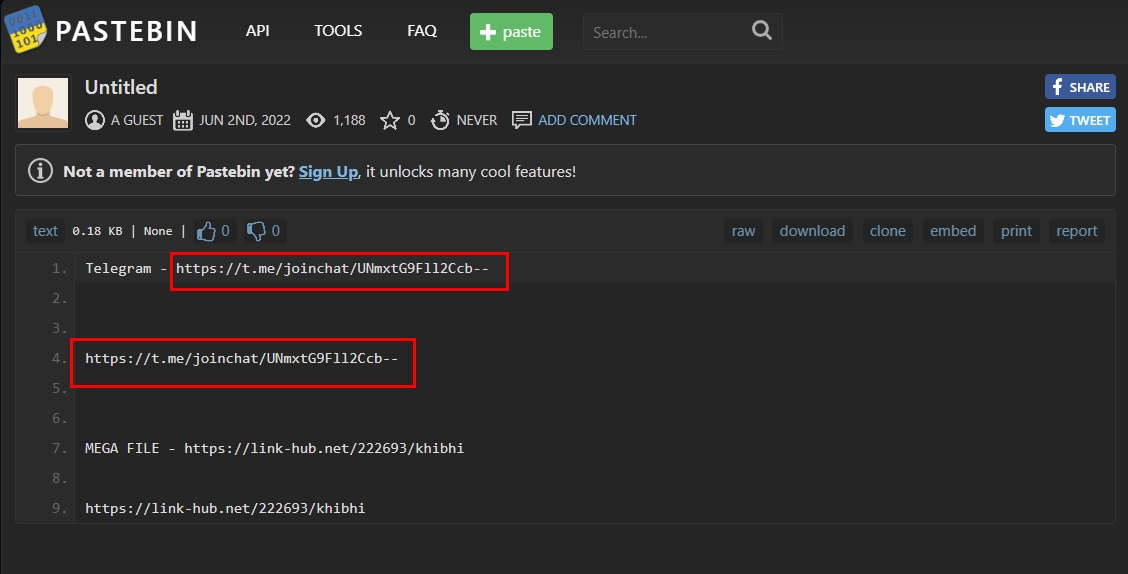
Figure 6 - Search for Telegram invite links in a specific website, in this example, I'm searching within the Pastebin.com website
- "t.me/joinchat/" OR "t.me/+" filetype:txt | Search for Telegram invite links in text files. This can reveal Telegram group links in publicly exposed .txt files (see Figure 7).
For more on Google dorking, check out our comprehensive guide.
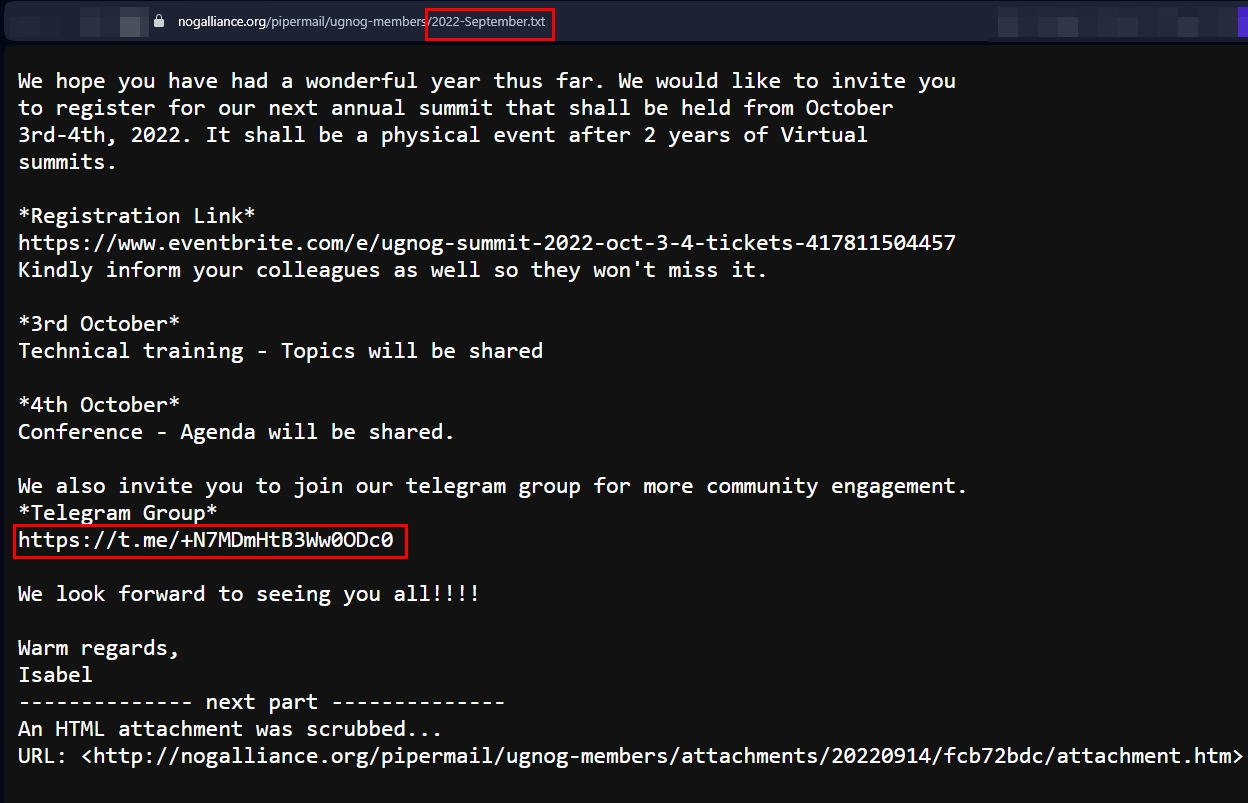
Figure 7 - Find Telegram invite links in exposed text files
Inspecting Telegram groups and channels contents
Telegram channels and groups contain different types of content, such as images, videos and text content. Here is how to inspect each type:
Text content analysis
We should begin by extracting usernames, emails, phone numbers and URLs mentioned in messages. We can use automated tools to scrape Telegram data. Here are some tools to perform this:
- Telegram-scraper – is a Python script built on Telethon for extracting messages and media from Telegram channels. It supports real-time scraping, media downloads and structured data export.
- Telegram Member Scraper – Scrape members info (name, username, bio, etc.) from Telegram "Groups/Channels".
Next, we must analyze the language patterns to determine user origin or demographics. For example, “mate” suggests British or Australian English, while “y’all” points to Southern U.S. English. On the other hand, non-English terms (e.g., “che” in Argentine Spanish) can pinpoint specific countries or regions.
Age or education level sometimes influence word choice. Younger users might use internet slang (e.g., “LOL,” “GOAT”), while highly educated users may use formal or technical language.
Grammatical structures reveal additional origin clues. Indian English speakers tend to prefer progressive constructions ("I am knowing"), whereas American English defaults to simple present ("I know"). These syntactical variations create recognizable fingerprints that help pinpoint user demographics with remarkable precision.
We can use automated tools to identify linguistic patterns in Telegram text messages, such as:
- Natural Language Toolkit – A Python library for NLP tasks like tokenization, part-of-speech tagging, sentiment analysis and word frequency analysis.
- spaCy – A Python NLP library for advanced text analysis, including named entity recognition (NER), dependency parsing and lemmatization. Identifies proper nouns (e.g., cities, events) that hint at the user's origin.
We can also use artificial intelligence (AI) technology to perform sentiment analysis on text posts to identify a piece of text's emotional tone (positive, negative or neutral). Here are some free tools:
Image inspection techniques
For all images that we want to inspect on the Telegram platform, we should follow these steps:
- Save images and perform reverse image searches using different search engines.
- Extract EXIF data from uncompressed images for location, device and time metadata. Here are some tools to reveal images' EXIF metadata:
- EXIF.tools
- ExifTool by Phil Harvey
- Exif Viewer | Firefox add-on
- Look for distinct landmarks, signage or environmental features for geolocation
- Analyze text visible in images through OCR tools. Here are some free OCR tools:
- NAPS2
- IMAGE TO TEXT CONVERTER - OCR ONLINE
- Check for digital watermarks or embedded signatures
Video content examination
Extract video frames for granular image-level examination. Audio components often reveal critical contextual markers through background sounds. Visual elements warrant particular scrutiny — we should note identifying features such as vehicle registrations, public signage or distinctive architectural characteristics. Technical metadata analysis of video quality specifications and formatting can identify the recording device with considerable precision. Here are some tools for extracting video metadata: metadata2go, Free Online EXIF & Metadata Viewer
NeedleStack Podcast: Telegram Intelligence Insights
On an episode of NeedleStack,SANS instructor Stephen Harris reveals Telegram's pivotal role in contemporary intelligence gathering. Originally a messaging platform, Telegram now functions as the primary information source for Ukraine/Russia conflict actors, with over half the population in both countries using it as their primary news channel.
Threat actors gravitate toward Telegram's non-cooperative stance with law enforcement, creating an environment where cybercriminal activities — database trading, DDoS coordination and attack claims — flourish with minimal disruption. Notable Russian hacking collectives (Hacknet, Beregini, NoName) leverage Telegram channels as operational PR wings.
Harris emphasizes investigative fundamentals over tools: proper intelligence planning, careful gap identification and bias mitigation (avoiding confirmation bias, availability errors, and tool fixation) determine investigation success. Specialized resources like Telegargo and Telepathy enhance Telegram research capabilities.
Most critically, Harris advocates for persistent curiosity in digital investigations — the technological landscape continuously evolves, requiring investigators to maintain adaptability and problem-solving mindsets.
Ready to level up your SOCMINT research?
Now that you have Telegram under your belt, download our comprehensive guide for social media intelligence gathering and analysis. This information-packed white paper gives the tradecraft and tools you need to find your targets.
For more SOCMINT tools and tradecraft, get the SOCMINT guide.
Telegram OSINT FAQs
What is Telegram OSINT?
Telegram OSINT refers to collecting and analyzing open-source intelligence from Telegram channels, groups, and profiles. Analysts use specialized tools to extract usernames, metadata, and behavioral patterns for investigation.
How can OSINT analysts collect data from Telegram?
OSINT analysts collect Telegram data using bots, scrapers, and search engines like Lyzem and Intelx. They extract messages, usernames, and images for digital profiling and cross-platform correlation.
What tools are best for Telegram investigations?
Top tools for Telegram investigations include Telepathy, Tosint, Telegram-scraper, and Sherlock. These applications help analysts extract usernames, Telegram IDs, and other metadata crucial for intelligence gathering.
How do you find Telegram channels for OSINT research?
Use Telegram search engines like XTEA.io, Telemetryapp, and Lyzem to find public channels and groups. You can also use Google dorks such as site:t.me "keyword" to locate specific Telegram links.
What is a Telegram numeric ID and why is it important?
A Telegram numeric ID is a permanent unique identifier for each account. Unlike usernames, it never changes, making it valuable for tracking users across Telegram activities and external databases.
Is Telegram suitable for SOCMINT investigations?
Yes, Telegram is one of the top platforms for SOCMINT investigations due to its public channels, group accessibility, and large user base, making it ideal for monitoring threat actor communication.
Tags OSINT research Social media Threat intelligence

