Stay up to date the most pressing cyber threats, emerging trends and what they mean for enterprise security, critical infrastructure and global risk.
TLP: CLEAR
Executive Summary
Several current critical cyber incidents demand immediate action. Industrial control system vulnerabilities require emergency patching by June 6, with CISA-rated critical flaws (CVSS 9.8) enabling complete device takeover in Rockwell PowerMonitor systems deployed across critical infrastructure. Meanwhile, DragonForce ransomware cartel achieved complete managed service provider infiltration through SimpleHelp RMM exploitation, enabling simultaneous deployment across multiple customer networks representing the nightmare scenario where trusted tools become attack vectors. At the same time, SAP NetWeaver systems are suffering an ongoing compromise through CVE-2025-31324 (CVSS 10.0), with threat actors deploying webshells and maintaining persistent access to enterprise systems managing critical business processes.
Healthcare organizations are enduring their own unprecedented assault with at least 33 ransomware attacks causing month-long operational closures. Impacts cascade across sectors as industrial system compromises threaten safety-critical operations, supply chain attacks generate average losses of $12.7 million per incident, and healthcare disruptions delay life-critical treatments for thousands of patients.
Recommendations include implementing all emergency industrial system patches, conducting immediate MSP security audits, applying SAP NetWeaver updates, and establishing enhanced authentication protocols for healthcare data access before threat actors leveraging these vulnerabilities achieve persistent access that will challenge incident response. The convergence of industrial targeting, supply chain exploitation, and healthcare sector assault may represent a coordinated campaign to maximize operational disruption across critical infrastructure.
Top Stories
Critical Infrastructure Facing Emergency Exploitation Risk
CISA published emergency advisories for Rockwell Automation PowerMonitor 1000 Remote systems containing three critical vulnerabilities (CVSS 9.8) enabling remote code execution without authentication. The industrial power monitoring devices, deployed across manufacturing, energy, and transportation sectors, suffered exploitation attempts within 24 hours of disclosure on May 28 as flaws allow attackers to crash operations remotely or execute unwanted code on systems managing power monitoring of critical infrastructure. Low attack complexity and remote exploitation capabilities make these targets highly attractive to nation-state actors seeking to pre-position for potential hybrid warfare scenarios. Organizations should immediately update firmware released in December 2024, implement network segmentation for all industrial monitoring systems, and deploy enhanced monitoring for unusual power system behavior or unauthorized remote access attempts before the June 6 CISA-mandated deadline.
DragonForce Executes Devastating MSP Supply Chain Attack
DragonForce ransomware gang executed a sophisticated supply chain attack against an unnamed managed service provider, exploiting three vulnerabilities in SimpleHelp RMM tool (CVE-2024-57727, CVE-2024-57728, CVE-2024-57726) to deploy encryptors across multiple downstream customer networks simultaneously. Sophos incident response teams detected the initial suspicious SimpleHelp installer deployment, but multiple customers suffered ransomware encryption and data theft from double-extortion operations before containment. This attack demonstrates the nightmare scenario where trusted management tools become attack vectors and threat actors recognize the economic benefits of compromising one MSP to ransom dozens of victims. Organizations should immediately audit all remote monitoring and management tools, implement network segmentation between RMM systems and production networks, enable MFA on all RMM accounts, and review access logs for the past 90 days for unauthorized connections or unusual activity patterns.
SAP NetWeaver Zero-Day Enables Enterprise-Wide Compromise
SAP Visual Composer component for NetWeaver systems suffers active exploitation through CVE-2025-31324 (CVSS 10.0), allowing unauthenticated file uploads resulting in immediate full system compromise. ReliaQuest and Onapsis researchers documented threat actors deploying webshells between March 14-31, 2025, with successful compromises affecting enterprise resource planning systems managing critical business processes. Russian ransomware groups BianLian and RansomEXX were tied to the initial exploitation waves, with additional attacks from Qilin group during the pre-patch period. SAP released emergency Security Note 3604119 addressing CVE-2025-42999 (CVSS 9.1) on May 13, fixing the root cause vulnerability. Organizations running SAP NetWeaver should immediately apply patches, conduct forensic analysis for webshell indicators, and implement enhanced monitoring for unauthorized file uploads or suspicious administrative activities on business-critical ERP systems.
Healthcare Sector Suffers Record Ransomware Assault
Healthcare facilities have endured at least 33 ransomware attacks in early 2025 with catastrophic operational impact, causing month-long closures and life-threatening treatment delays. Michigan State University research revealed that ransomware drives 69% of all healthcare data breaches despite representing only 11% of incidents by count, exposing 285 million patient records over 15 years. Average healthcare data breach costs reached $9.77 million - the highest of any sector for the 14th consecutive year - while recovery times extend beyond one month for critical care systems. Threat actors specifically target healthcare due to life-critical operations increasing payment probability, Protected Health Information (PHI) commanding $250-$400 per record on dark web markets, and legacy systems providing easy initial access. Healthcare organizations should immediately implement 72-hour offline operational capabilities for critical care systems, maintain physically isolated backup networks for patient care continuity, and establish pre-negotiated incident response retainers including ransomware negotiation expertise.
CISA Advisory Changes Create Visibility Gaps
CISA announced, then paused, controversial changes to cybersecurity advisory distribution, initially planning to stop publishing standard updates on public webpages in favor of email and social media distribution. The proposed changes triggered widespread concern from security professionals who rely on automated RSS feeds and GitHub repositories for threat intelligence integration into security operations centers. Following industry backlash, CISA acknowledged confusion and paused implementation while reassessing distribution approaches. The temporary uncertainty created visibility gaps for smaller security teams lacking dedicated threat intelligence staff and potentially disrupted automated security alert systems. Organizations should implement backup threat intelligence sources so security operations teams can maintain situational awareness through alternative government and vendor channels.
Top Threats
Chinese Ministry of State Security Coordination Campaign
Chinese state-sponsored groups demonstrated unprecedented coordination as APT40, Mustang Panda, and APT41 units conducted synchronized campaigns against US critical infrastructure with a 136% activity increase between October 2024 and March 2025. Technical analysis reveals infrastructure investment exceeding $10 million, custom malware compilation per victim, and legitimate cloud service abuse for command-and-control operations. Their collection priorities focus on telecommunications provider CALEA interfaces, defense contractor supply chains, and semiconductor technology companies aligning with China's 14th Five-Year Plan for technological self-sufficiency. The groups' hallmark patience, signified by their average 18-month presence before data exfiltration, indicates strategic intelligence collection supporting People's Liberation Army (PLA) modernization requirements rather than immediate operational disruption.
Russian GRU Logistics Warfare Campaign
APT28 (Fancy Bear) sustained multi-year campaigns targeting Western logistics and technology firms supporting Ukraine aid delivery, with particular focus on Ukrainian border regions and NATO member states. Their evolution from crude spearphishing to sophisticated living-off-the-land techniques demonstrates significant operational security improvements, leveraging compromised edge devices and legitimate cloud services for command-and-control. Recent technical analysis reveals custom toolsets designed for long-term persistence and supply chain mapping rather than immediate disruption, suggesting intelligence collection supporting Russian military hybrid warfare objectives. The group's trademark precision in victim selection, combined with 180-day average dwell time, requires defenders to assume persistent presence and implement retrospective threat hunting.
DragonForce Ransomware-as-a-Service Cartel
DragonForce emerged as a dominant ransomware operation offering white-label models allowing affiliates to deploy rebranded encryptors, democratizing sophisticated attack capabilities since their 2023 debut. Their business model innovation extends beyond technology to operational sophistication: tiered affiliate programs with 20-30% commission, dedicated negotiation teams, and reputation management through "customer service" portals. Technical analysis reveals custom encryption per victim, data exfiltration before encryption ensuring leverage, and systematic targeting of managed service providers for maximum cascading impact. Their success attracts top-tier affiliates from disbanded groups like LockBit and ALPHV, concentrating expertise and accelerating victimization rates across critical infrastructure sectors through supply chain exploitation.
Iranian Enhanced Social Engineering Operations
APT42 (Charming Kitten) demonstrated heavy utilization of commercial AI tools, accounting for over 30% of Gemini usage by nation-state actors for crafting phishing campaigns and conducting reconnaissance against defense organizations. Their enhanced social engineering schemes evolved from traditional credential harvesting to persistent cloud infrastructure compromise through multi-month relationship building before deploying custom backdoors like HanifNet and NeoExpressRAT. Recent campaigns utilized AI for content creation, translation, and localization supporting influence operations against Western democratic processes. These operations likely support Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) collection requirements against critical national infrastructure, suggesting potential pre-positioning for future strategic advantage during regional conflicts.
North Korean Financial Systematic Operations
Lazarus Group and TraderTraitor units operate under direct state tasking for systematic revenue generation supporting regime priorities including weapons development programs.⁹ Their expansion beyond traditional cryptocurrency theft includes supply chain attacks against AI/blockchain companies, fake recruitment campaigns targeting developers, and social engineering operations requiring months of relationship building before payload delivery. Recent operations demonstrate unprecedented sophistication including voice synthesis for authentication bypass, deepfake video meetings for financial fraud, and systematic targeting of cryptocurrency exchange-traded funds for pre-operational reconnaissance.
Top Trends
Zero-Day Weaponization Speed Acceleration
The gap between vulnerability disclosure and active exploitation collapsed dramatically in Q1 2025, with 28.3% of CVEs exploited within 24 hours as compared to the historical 32-day average weaponization timeline.¹⁰ Nation-state actors discovered 61% of zero-days but criminal adoption accelerated through underground markets where exploits are priced at 40% premiums over 2024 levels. This compressed timeline breaks traditional monthly patch cycles, leaving organizations with guaranteed 11-day exposure windows for critical vulnerabilities. The democratization of advanced capabilities previously restricted to nation-states, enabled by cryptocurrency payments and anonymous markets, forces defenders to plan for inevitable compromise rather than rely on patch-and-pray strategies.
AI-Enhanced Social Engineering Evolution
Voice phishing attacks increased 442% between first and second halves of 2024, driven by AI-generated impersonation tactics creating convincing audio clones with minimal sample data.¹¹ Success rates tripled versus conventional approaches while defensive detection tools struggle with 43% false positive rates creating alert fatigue. Advanced social engineering that previously required language skills and cultural knowledge is now available through simple prompts. Real-time voice synthesis enables vishing attacks indistinguishable from legitimate calls, while coordinated campaigns combine email, voice, and video for multi-channel authentication bypass. AI-powered phishing currently only represents 0.7% to 4.7% of attack, but we can expect that to grow exponentially as technical barriers disappear and the ROI for these scams increases
Supply Chain Attack Multiplication Effect
Supply chain attacks against MSPs grew 267% in Q1 2025 versus prior year, with managed service providers comprising 73% of initial access vectors for cascading compromises. The multiplier effect results in an average of 47 downstream victims per compromise, 94-day dwell time before detection, and $12.7 million average losses (4.3x higher than direct attacks). Global annual costs from software supply chain attacks are projected to hit $60 billion in 2025 and grow to $138 billion by 2031. Attacks on MSPs fundamentally challenge managed service models where vendor security postures directly determine customer risk exposure through shared infrastructure and admin access.
Cryptocurrency Theft Industrialization Trajectory
Global cryptocurrency theft approaches $2.2 billion for 2025 (21% increase from 2023), with North Korean state actors responsible for 61% of total value despite representing only 20% of incidents. The shift from traditional mixing services to sophisticated cross-chain bridges and decentralized exchanges indicates expanded money laundering infrastructure enabling rapid dispersion across thousands of blockchain addresses. This industrialization systematically funds weapons development programs while building sanctions-resistant financial reserves, positioning North Korea to exploit alternative payment systems being developed by China and Russia. Cryptocurrency theft now surpasses traditional cybercrime revenue streams, attracting increased nation-state participation and professionalizing criminal operations.
Ransomware Healthcare Targeting Intensification
Healthcare ransomware attacks increased to at least 33 incidents in early 2025, with Michigan State University research revealing ransomware drives 69% of all healthcare data breaches exposing 285 million patient records over 15 years. Average healthcare data breach costs reached $9.77 million - the highest of any sector for 14 consecutive years - while recovery times extend beyond one month for critical care systems. Threat actors systematically target healthcare due to intersection of factors: life-critical operations increase payment probability, Protected Health Information commands premium dark web prices ($250-$400 per record), and legacy systems provide easy initial access. The human cost extends beyond finances with cancer treatments delayed, emergency services diverted, and surgical schedules destroyed, making healthcare the most attractive ransomware target due to operational pressure to pay.
Top Vulnerabilities
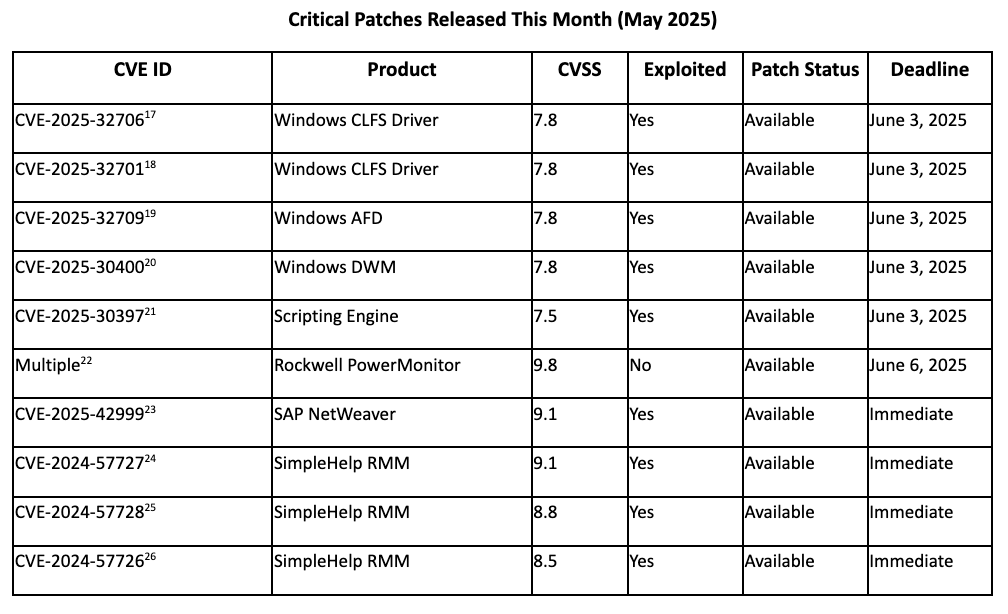
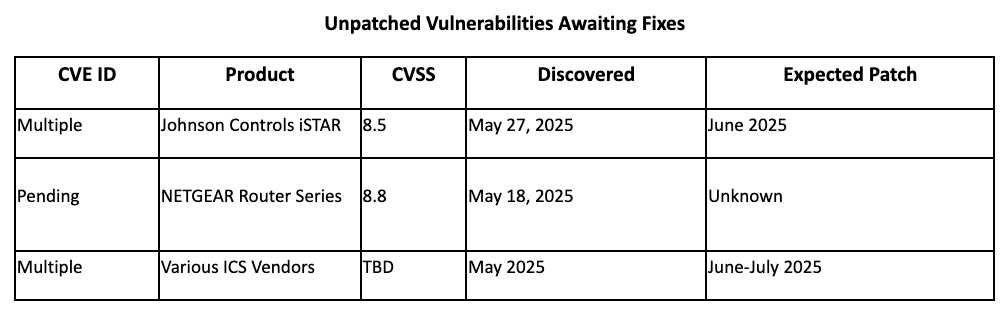
Recommended Immediate Actions
Critical Industrial System Emergency Response
Immediately identify and patch all Rockwell PowerMonitor 1000 Remote systems before June 6 CISA deadline, prioritizing energy generation, manufacturing control, and transportation management installations. If immediate patching isn't feasible, implement emergency network segmentation isolating power monitoring systems from corporate networks, disable remote access capabilities, and deploy continuous monitoring for Event IDs indicating unauthorized system access or configuration changes.
SAP NetWeaver Incident Response
Conduct emergency forensic analysis of all SAP NetWeaver systems for webshell indicators from March 2025 exploitation period, focusing on Visual Composer components and file upload directories. Apply CVE-2025-42999 patches immediately, implement enhanced monitoring for unauthorized file uploads, and establish incident response procedures for business-critical ERP system compromises that could disrupt financial operations and supply chain management.
MSP Relationship Security Audit
Audit all managed service provider relationships within 24 hours, particularly those using SimpleHelp, ConnectWise, or Kaseya RMM tools. Implement immediate network segmentation between MSP access points and production systems, mandate MFA on all vendor accounts, review 90-day access logs for suspicious patterns, and establish emergency disconnection procedures for vendor access during security incidents.
Each week, we share the most pressing cyber threats, emerging trends and what they mean for enterprise security, critical infrastructure and global risk. To keep up to date, follow us on LinkedIn.
- Bank Info Security. Popular industrial power monitors had remote hacking flaws. Bank Info Security website. Published May 28, 2025. https://www.bankinfosecurity.com/popular-industrial-power-monitors-had-remote-hacking-flaws-a-28522
- Dark Reading. DragonForce ransomware strikes MSP in supply chain attack. Dark Reading website. Published May 27, 2025. https://www.darkreading.com/application-security/dragonforce-ransomware-msp-supply-chain-attack
- Onapsis. CVE-2025-31324 SAP zero-day vulnerability full threat brief. Onapsis website. Published May 28, 2025. https://onapsis.com/blog/active-exploitation-of-sap-vulnerability-cve-2025-31324/
- MSU Today. MSU study: ransomware drives US health data breaches. MSU Today website. Published May 15, 2025. https://msutoday.msu.edu/news/2025/msu-study-ransomware-drives-us-health-data-breaches
- Bank Info Security. Popular industrial power monitors had remote hacking flaws. Bank Info Security website. Published May 28, 2025. https://www.bankinfosecurity.com/popular-industrial-power-monitors-had-remote-hacking-flaws-a-28522
- Security Magazine. Cyberattacks targeting US increased by 136%. Security Magazine website. Published April 2025. https://www.securitymagazine.com/articles/101596-cyberattacks-targeting-us-increased-by-136
- Onapsis. CVE-2025-31324 SAP zero-day vulnerability full threat brief. Onapsis website. Published May 28, 2025. https://onapsis.com/blog/active-exploitation-of-sap-vulnerability-cve-2025-31324/
- MSU Today. MSU study: ransomware drives US health data breaches. MSU Today website. Published May 15, 2025. https://msutoday.msu.edu/news/2025/msu-study-ransomware-drives-us-health-data-breaches
- Infosecurity Magazine. CISA reverses decision on cybersecurity advisory changes. Infosecurity Magazine website. Published May 14, 2025. https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/news/cisa-reverses-decision-advisory/
- Security Magazine. Cyberattacks targeting US increased by 136%. Security Magazine website. Published April 2025. https://www.securitymagazine.com/articles/101596-cyberattacks-targeting-us-increased-by-136
- GovTech. Midyear roundup: nation-state cyber threats in 2025. GovTech website. Published May 25, 2025. https://www.govtech.com/blogs/lohrmann-on-cybersecurity/midyear-roundup-nation-state-cyber-threats-in-2025
- Dark Reading. DragonForce ransomware strikes MSP in supply chain attack. Dark Reading website. Published May 27, 2025. https://www.darkreading.com/application-security/dragonforce-ransomware-msp-supply-chain-attack
- The Hacker News. Google: over 57 nation-state threat groups using AI for cyber operations. The Hacker News website. Published January 31, 2025. https://thehackernews.com/2025/01/google-over-57-nation-state-threat.html
- Dark Reading. DragonForce ransomware strikes MSP in supply chain attack. Dark Reading website. Published May 27, 2025. https://www.darkreading.com/application-security/dragonforce-ransomware-msp-supply-chain-attack
- FBI. North Korea responsible for $1.5 billion Bybit hack. FBI Internet Crime Complaint Center website. Published February 26, 2025. https://www.ic3.gov/PSA/2025/PSA250226
- MSU Today. MSU study: ransomware drives US health data breaches. MSU Today website. Published May 15, 2025. https://msutoday.msu.edu/news/2025/msu-study-ransomware-drives-us-health-data-breaches
- CrowdStrike. May 2025 patch Tuesday: updates and analysis. CrowdStrike website. Published May 14, 2025. https://www.crowdstrike.com/en-us/blog/patch-tuesday-analysis-may-2025/
- CrowdStrike. May 2025 patch Tuesday: updates and analysis. CrowdStrike website. Published May 14, 2025. https://www.crowdstrike.com/en-us/blog/patch-tuesday-analysis-may-2025/
- CrowdStrike. May 2025 patch Tuesday: updates and analysis. CrowdStrike website. Published May 14, 2025. https://www.crowdstrike.com/en-us/blog/patch-tuesday-analysis-may-2025/
- CrowdStrike. May 2025 patch Tuesday: updates and analysis. CrowdStrike website. Published May 14, 2025. https://www.crowdstrike.com/en-us/blog/patch-tuesday-analysis-may-2025/
- CrowdStrike. May 2025 patch Tuesday: updates and analysis. CrowdStrike website. Published May 14, 2025. https://www.crowdstrike.com/en-us/blog/patch-tuesday-analysis-may-2025/
- Bank Info Security. Popular industrial power monitors had remote hacking flaws. Bank Info Security website. Published May 28, 2025. https://www.bankinfosecurity.com/popular-industrial-power-monitors-had-remote-hacking-flaws-a-28522
- Onapsis. CVE-2025-31324 SAP zero-day vulnerability full threat brief. Onapsis website. Published May 28, 2025. https://onapsis.com/blog/active-exploitation-of-sap-vulnerability-cve-2025-31324/
- Dark Reading. DragonForce ransomware strikes MSP in supply chain attack. Dark Reading website. Published May 27, 2025. https://www.darkreading.com/application-security/dragonforce-ransomware-msp-supply-chain-attack
- Dark Reading. DragonForce ransomware strikes MSP in supply chain attack. Dark Reading website. Published May 27, 2025. https://www.darkreading.com/application-security/dragonforce-ransomware-msp-supply-chain-attack
- Dark Reading. DragonForce ransomware strikes MSP in supply chain attack. Dark Reading website. Published May 27, 2025. https://www.darkreading.com/application-security/dragonforce-ransomware-msp-supply-chain-attack


