This week’s Cyber Intel Brief covers Cisco ASA zero-day exploits with ROM-level persistence, major supply chain breaches and ransomware operations moving faster than ever.
27 September – 3 October 2025 | TLP: CLEAR
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
The week ending 3 October 2025 included significant coordinated cybersecurity responses among Five Eyes nations triggered by active nation-state exploitation of Cisco network infrastructure with ROM-level persistence capabilities. CISA Emergency Directive 25-03 ordered immediate federal agency action while Canadian, Australian, and UK cybersecurity agencies issued parallel warnings within 24 hours, demonstrating maturation of international threat intelligence sharing. The ArcaneDoor campaign's ability to survive factory resets through ROM manipulation represents a fundamental advancement in threat actor tradecraft that challenges standard incident response procedures.
Multiple supply chain compromises during the collection period exposed systematic targeting of software development pipelines. The Shai-Hulud campaign compromised npm ecosystem packages with 2.2 million weekly downloads, evolved through seven malware variants, and specifically targeted CrowdStrike-maintained packages affecting security vendor supply chains. Red Hat GitLab breach exposed 570GB across 28,000 repositories containing CI/CD secrets for Citigroup, JPMorgan Chase, HSBC, Verizon, Siemens, and U.S. Senate, creating cascading authentication risks across dozens of high-value targets. Oracle E-Business Suite customers received mass extortion emails from Clop ransomware operators exploiting July 2025 vulnerabilities, with threat actors using hundreds of compromised accounts from infostealer logs to enhance credibility.
Nation-state operations demonstrated sustained targeting of telecommunications and critical infrastructure. Chinese APT group Salt Typhoon compromised telecommunications providers across United States, United Kingdom, and Europe with custom Demodex rootkit targeting lawful intercept systems and call detail records. Iranian APT35 exploited CVE-2023-23397 to compromise defense ministry networks through SSPI credential harvesting. North Korean fraudulent IT worker operations expanded to 27 countries beyond technology sector, with Okta research documenting 6,500+ job interviews across 5,000 companies over four years. Critical infrastructure faced ransomware disruptions including Collins Aerospace MUSE system affecting Brussels, Berlin, and London Heathrow airports, Asahi Group production suspension impacting 40% of Japan's beer market, and Akira ransomware achieving hour-long dwell times through SonicWall SSL VPN exploitation.
Intelligence collection yielded 18 vulnerabilities added to CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog, including CVSS 10.0 Fortra GoAnywhere MFT flaw exploited eight days before public disclosure and VMware Tools privilege escalation exploited as zero-day since October 2024. Federal agencies face October 20 remediation deadline for five KEV additions from 29 September while navigating compliance with passed 26 September deadline for Cisco ASA/FTD patches. MS-ISAC federal funding termination effective 1 October eliminates $27 million annual support for 18,000+ state, local, tribal, and territorial government organizations, creating operational gaps during period of heightened infrastructure targeting.
Analyst Comment: The convergence of nation-state infrastructure exploitation, supply chain compromises targeting developer ecosystems, critical infrastructure ransomware, and U.S. federal cybersecurity operational disruptions creates compounding risk requiring immediate defensive action. Organizations must prioritize patching actively exploited vulnerabilities before October 20 federal deadline, implement supply chain security controls for software development pipelines, migrate to phishing-resistant MFA, and enhance third-party vendor security assessments. The week's intelligence demonstrates threat actors successfully targeting every layer of enterprise infrastructure from network perimeter devices through software supply chains to end-user applications.
CRITICAL INCIDENTS
1. ArcaneDoor Campaign: Nation-State Exploitation of Cisco Infrastructure with ROM Persistence
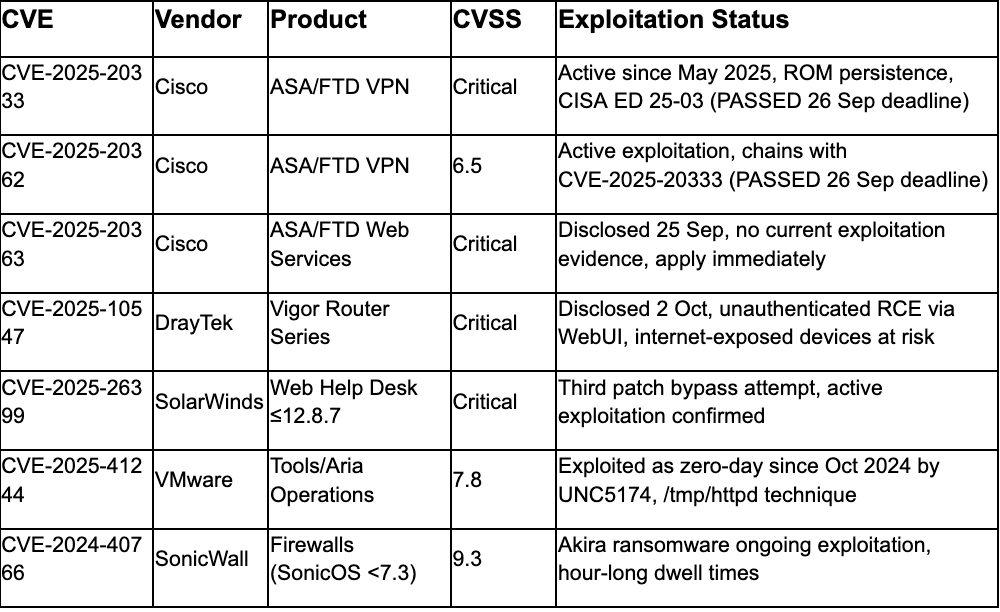
ArcaneDoor threat actor exploited CVE-2025-20333 and CVE-2025-20362 in Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance and Firepower devices since May 2025, achieving unauthenticated remote code execution with Read-Only Memory Monitor (ROMMON) manipulation enabling persistence through reboots, firmware upgrades, and factory reset procedures.¹'² CISA issued Emergency Directive 25-03 on 25 September requiring federal agencies to collect memory core dumps by 26 September, apply patches by 26 September, disconnect end-of-support devices by 30 September, and report complete inventories by 2 October.² CVE-2025-20333 enables arbitrary code execution as root through buffer overflow in VPN web server requiring valid VPN credentials, while CVE-2025-20362 provides missing authorization allowing unauthenticated access to restricted URL endpoints enabling chaining for full unauthenticated remote code execution.³
UK National Cyber Security Centre released malware analysis for RayInitiator and LINE VIPER implant families associated with campaign, documenting ROM modification techniques enabling malware survival through standard remediation procedures.² Analysis indicates ArcaneDoor primarily targets ASA 5500-X Series platforms lacking Secure Boot and Trust Anchor capabilities, with over 48,800 internet-exposed Cisco ASA/FTD devices remaining vulnerable as of September 2025.³'¹⁰ Cisco and CISA assess with high confidence campaign attribution to ArcaneDoor threat actor group (UAT4356), representing nation-state capabilities with sustained operational security enabling five-month exploitation window before detection.¹'²
Analyst Comment: ROM-level persistence represents significant threat actor tradecraft evolution challenging fundamental assumptions about hardware trust boundaries and factory reset efficacy. Organizations using affected Cisco devices must prioritize ED 25-03 compliance including forensic core dump analysis even on patched systems to detect potential historical compromise. The five-month exploitation window before disclosure demonstrates sophisticated operational security, while ROMMON manipulation capability suggests threat actor investment in persistence mechanisms surviving standard incident response procedures. Legacy hardware lacking Secure Boot capabilities presents elevated risk requiring accelerated hardware refresh planning.
2. Red Hat GitLab Breach Exposes Enterprise Secrets Across Financial and Government Sectors
Crimson Collective threat actors exfiltrated approximately 570GB from 28,000 private GitLab repositories belonging to Red Hat Consulting team, compromising CI/CD secrets, pipeline configurations, VPN profiles, infrastructure blueprints, Ansible playbooks, OpenShift deployment guides, container registry configurations, and Vault integration secrets.⁴ Stolen data references major organizations including Citigroup, JPMorgan Chase, HSBC, Verizon, Telefónica, Siemens, Bosch, and U.S. Senate, creating secondary attack vectors through exposed SSH keys, API tokens, and database connection strings. Red Hat isolated compromised GitLab instance and contacted law enforcement, confirming incident occurred independently of CVE-2025-10725 vulnerability indicating targeted compromise rather than opportunistic exploitation.⁴
Breach impacts financial services, telecommunications, industrial manufacturing, and government sectors through consulting engagement documentation containing production environment credentials and architectural blueprints. Exposed Ansible playbooks reveal automation workflows and privileged account structures, while container registry configurations provide insights into application deployment patterns and potential supply chain injection points. VPN profiles and SSH keys enable direct network access to client environments, while Vault integration secrets compromise credential management systems protecting additional authentication material.⁴
Analyst Comment: Supply chain targeting of consulting firm repositories provides threat actors with authentication credentials and architectural knowledge for dozens of high-value targets simultaneously, representing force multiplication attack vector. The 28,000 repository compromise scale suggests systematic exfiltration rather than selective targeting, indicating threat actor intent to maintain long-term access options across multiple victim organizations. Red Hat Consulting clients must immediately rotate all credentials and secrets, audit GitLab repositories for unauthorized access indicators, hunt for usage of compromised SSH keys and API tokens in network logs, review container deployment manifests for unauthorized changes, implement additional monitoring on systems referenced in stolen blueprints, and engage incident response teams for comprehensive forensic analysis.
3. Shai-Hulud Campaign: npm Ecosystem Supply Chain Attack Affecting 500+ Packages
September 2025 supply chain attack compromised @ctrl/tinycolor npm package (2.2 million weekly downloads) affecting over 40 packages initially, expanding to nearly 500 packages including CrowdStrike-maintained packages.⁵ Malicious update injected bundle.js script trojanizing downstream packages to harvest developer and cloud credentials using TruffleHog, create GitHub Actions workflows, and exfiltrate sensitive data to attacker-controlled endpoints. Investigation revealed attackers validated npm tokens via whoami endpoint and integrated with GitHub APIs exploiting automated workflows for systematic data theft, with malicious payload executing automatically upon package installation targeting tokens, CI credentials, and cloud metadata.⁵
CrowdStrike npm supply chain attack represents significant escalation beyond @ctrl/tinycolor compromise, with attackers publishing more than 500 malicious packages under CrowdStrike-publisher account.⁵ Core payload bundle.js remained consistent for secret scanning and exfiltration but evolved through multiple variants (v1-v7) refining tactics by reducing noise, modifying credential checks, and altering workflow logic improving stealth capabilities. Unlike Tinycolor attack on popular open-source dependency, CrowdStrike compromise demonstrates deliberate focus on high-value security vendor packages. Evolution from isolated opportunistic compromises into sustained large-scale assault on critical ecosystems demonstrates threat maturation, with CrowdStrike customers facing elevated supply chain risk.⁵
Analyst Comment: Concentration of npm supply chain attacks targeting both high-download-count packages and security vendor ecosystems within single campaign demonstrates sophisticated understanding of software supply chain dependencies and trust relationships. The seven-variant evolution of bundle.js payload indicates active threat actor refinement responding to detection attempts and optimizing credential harvesting efficiency. Organizations must immediately audit all npm packages for @ctrl/tinycolor dependencies and malicious bundle.js variants, rotate all npm tokens and GitHub credentials, review GitHub Actions workflows for unauthorized modifications, block identified exfiltration endpoints, implement npm package integrity verification, deploy supply chain security scanning, monitor for TruffleHog credential scanning attempts, and audit CI/CD pipelines for compromised secrets.
4. Oracle E-Business Suite Mass Extortion Campaign Leveraging July 2025 Vulnerabilities
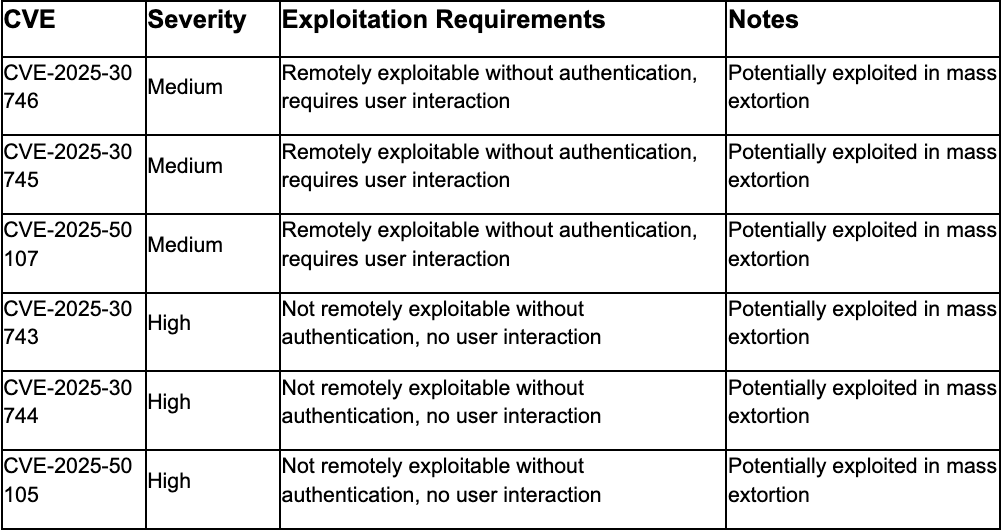
Clop ransomware group sent extortion emails to Oracle E-Business Suite customers claiming data theft through exploitation of vulnerabilities addressed in July 2025 Critical Patch Update.⁶ Emails originated from hundreds of compromised third-party accounts using credentials harvested from infostealer malware logs. Oracle investigation identified potential exploitation of CVE-2025-30746, CVE-2025-30745, CVE-2025-50107 (medium severity, remotely exploitable without authentication but requiring user interaction) and CVE-2025-30743, CVE-2025-30744, CVE-2025-50105 (high severity, not remotely exploitable without authentication but no user interaction required). Extortion messages claim to originate from Cl0p ransomware group, with emails sent from compromised accounts previously linked to FIN11 cybercrime gang. Google Threat Intelligence Group and Mandiant investigating but have not confirmed data theft claims, while both Cl0p and FIN11 historically exploit zero-days in file transfer products (Cleo, MOVEit, Fortra, Accellion) for mass extortion campaigns.⁶
Analyst Comment: Mass extortion campaigns leveraging compromised email accounts for credibility represent tactical evolution in ransomware group operations, exploiting trust relationships between legitimate organizations. The use of infostealer-harvested credentials for extortion distribution demonstrates downstream consequences of commodity malware infections extending beyond initial compromise. Oracle E-Business Suite customers must apply July 2025 Critical Patch Update immediately, review access logs for unauthorized patterns dating to July 2025, implement enhanced logging on E-Business Suite instances, restrict E-Business Suite exposure to internet, hunt for unusual authentication patterns or data exfiltration attempts, and engage incident response if extortion emails received. Organizations should not pay ransoms without confirming legitimate breach through forensic analysis.
5. Salt Typhoon: Chinese State-Sponsored Telecommunications Infrastructure Campaign
Chinese state-sponsored group Salt Typhoon conducting cyber espionage campaign targeting global telecommunications infrastructure since late 2024, focusing on routers, firewalls, VPN gateways, and lawful intercept systems affecting telecommunications providers in United States, United Kingdom, and Europe.⁷ Operations exploit CVE-2023-20198 (Cisco IOS XE) and CVE-2023-35082 (Ivanti Connect Secure) for initial access, deploying custom firmware rootkit "Demodex" surviving reboots and evading detection. Domaintools identified distinctive infrastructure using fabricated U.S. personas and ProtonMail for WHOIS entries, with malware establishing encrypted command-and-control channels via DNS beacons or HTTPS on TCP 443. Exfiltrated data includes lawful intercept logs, call detail records, and router configurations, with long-dwell persistence enabling potential communications disruption during geopolitical crises.⁷
Analyst Comment: Targeting of lawful intercept systems represents intelligence collection against law enforcement and national security surveillance capabilities, providing insight into investigative targets and techniques. The Demodex rootkit's firmware-level persistence combined with exploitation of two-year-old vulnerabilities suggests either previously unpatched infrastructure or re-compromise following initial remediation. Telecommunications providers must patch CVE-2023-20198 and CVE-2023-35082 immediately, audit network edge devices for unauthorized firmware modifications, monitor for DNS beaconing and unusual HTTPS traffic patterns, inspect /usr/bin/ directories on routers for suspicious binaries, review startup scripts for persistence mechanisms, implement network segmentation between management and production networks, and enable enhanced logging on lawful intercept systems.
6. Akira Ransomware: Hour-Long Dwell Times via SonicWall SSL VPN Exploitation
Akira ransomware group continues exploiting CVE-2024-40766 (CVSS 9.3) improper access control vulnerability in SonicWall firewalls patched August 2024, with campaign remaining active targeting SSL VPN accounts using one-time password MFA.⁸ Arctic Wolf observed dozens of incidents characterized by VPN logins from VPS hosting providers, network scanning, Impacket SMB activity for endpoint discovery, and Active Directory reconnaissance, with dwell times measured in hours rather than days representing among shortest recorded for ransomware operations. Barracuda analysis revealed attackers leveraging Datto remote monitoring and management tool installed on domain controllers alongside pre-installed backup agents to evade detection, with attackers using legitimate utilities mimicking backup agent behavior during scheduled jobs making activity appear as regular IT operations.⁸
SonicWall confirmed devices running SonicOS versions prior to 7.3 susceptible to brute force attacks affecting MFA credentials, with multiple threat actors or affiliates likely involved using automation for authentication. Successful exploitation enables VPN access followed by rapid lateral movement, with attackers deploying Impacket for SMB enumeration and leveraging Datto RMM or backup agent installations on domain controllers for privileged execution. The combination of vulnerable SSL VPN, OTP-based MFA susceptibility, and legitimate RMM tool abuse enables compressed attack timelines from initial access to encryption deployment.⁸
Analyst Comment: Hour-long dwell times represent significant compression of typical ransomware kill chain, limiting detection and response windows. The exploitation of legitimate RMM tools installed on domain controllers demonstrates sophisticated understanding of enterprise IT operations and defensive blind spots around scheduled maintenance activities. Organizations must patch CVE-2024-40766 on all SonicWall devices immediately, upgrade SonicOS to version 7.3 or later, migrate from OTP-based MFA to phishing-resistant authentication (FIDO2, hardware tokens), monitor for VPN logins from VPS hosting provider ASNs, detect Impacket SMB traffic patterns on networks, audit Datto RMM and backup agent installations on domain controllers, implement behavioral monitoring distinguishing legitimate backup activity from malicious mimicry, review firewall rules for unauthorized modifications, enable enhanced logging on SSL VPN authentication, and restrict RMM tool access to authorized administrators only.
7. North Korean IT Worker Global Expansion: 27 Countries, 6,500+ Job Interviews
Okta Threat Intelligence research based on 130+ identities linked to 6,500+ job interviews across 5,000 companies over four years through mid-2025 reveals North Korean DeceptiveDevelopment campaign serves dual purpose: deploying malware while harvesting developer identities for fraudulent IT worker program tracked as WageMole.⁹ Nearly every industry duped into hiring North Koreans as technology represents only half of targeted victims, with workers now applying for remote finance positions and engineering roles. Global expansion documented across 27 countries with 27% of roles outside U.S. targeting UK, Canada, Germany (150-250 roles each) plus India, Australia, Singapore, Switzerland, Japan, France, Poland. Years of sustained activity refined infiltration methods entering new markets with mature workforce bypassing basic screening controls.⁹
Threat actors use fake recruiter profiles on LinkedIn, Upwork, and Freelancer.com to lure cryptocurrency developers with fake job offers, tricking victims during fake interviews into executing malware including BeaverTail, InvisibleFerret, OtterCookie, WeaselStore (GolangGhost/FlexibleFerret), PylangGhost, TsunamiKit, Tropidoor (shares code with Lazarus PostNapTea RAT), and AkdoorTea. Harvested identities enable WageMole IT workers to secure legitimate remote positions through proxy interviewing, stolen identities, and AI-generated synthetic identities. Operations target western countries primarily U.S. and European nations including France, Poland, Ukraine, Albania. Teams operate under dedicated "boss" leaders setting quotas and coordinating work, with workers pursuing programming jobs plus civil engineering and architecture positions, impersonating real companies and producing falsified engineering drawings with fake approval stamps.⁹
Analyst Comment: North Korean expansion beyond technology roles into finance and engineering positions indicates operational maturation and diversification of revenue generation and intelligence collection capabilities. The four-year operation spanning 6,500+ interviews demonstrates industrial-scale fraudulent employment scheme with sophisticated social engineering, identity theft, and malware deployment capabilities. Organizations should enhance screening for remote workers including video interviews with unexpected questions testing technical knowledge, verify identity documents through multiple channels, monitor for proxy interviewing indicators including audio/video discrepancies, implement behavioral analytics detecting unusual work patterns, review contractor vetting procedures for engineering and architecture roles, deploy endpoint detection hunting for BeaverTail, InvisibleFerret, Tropidoor, and AkdoorTea malware families, block fake recruiter domains and social media profiles, train developers on fake job offer social engineering tactics, and implement code signing and review processes detecting malicious commits from compromised accounts.
8. Collins Aerospace Ransomware Disrupts European Aviation Operations
Ransomware attack against Collins Aerospace's MUSE check-in and boarding system disrupted operations at key European hubs including Brussels, Berlin, and London Heathrow causing widespread delays and cancellations as airports fell back to manual processing.¹¹ ENISA confirmed ransomware with investigations continuing through days of residual disruption into September 23. Analyses highlighted single point-of-failure risk in aviation IT supply chains and heightened threat to critical infrastructure from organized cybercrime. UK authorities quickly arrested individual in connection with incident.¹¹
Analyst Comment: Single vendor system failure cascading across multiple international airports demonstrates critical infrastructure concentration risk in aviation sector. The rapid UK law enforcement response resulting in arrest suggests either domestic threat actor or strong international cooperation enabling swift attribution. Organizations providing critical aviation infrastructure must conduct business continuity assessments for single points of failure, implement redundant check-in and boarding systems, deploy enhanced ransomware detection on aviation-critical systems, review vendor security postures, maintain manual processing capability, conduct ransomware preparedness exercises, implement network segmentation, and deploy immutable backups.
9. Asahi Group Cyberattack Suspends Japanese Beer Production
Japanese brewing giant Asahi Group Holdings disclosed September 30, 2025 that cyberattack resulted in system failures affecting orders and shipments across all Japanese subsidiaries, with production suspended at multiple facilities among company's 30 domestic factories.¹² Call center operations and customer service desks impacted, with system failure limited to Japan operations. Company holds approximately 40% market share in Japanese beer market and owns international brands including Grolsch, Peroni, Pilsner Urquell, and Fullers (London Pride). System-wide outage pattern suggests file-encrypting ransomware deployment though company has not disclosed attack nature. No confirmed leakage of personal information or customer data reported, with company investigating incident and working on system restoration but unable to provide recovery timeline.¹²
Analyst Comment: Disruption confined to single country but represents costly production and supply chain halt for major manufacturing operation controlling 40% of national market. Manufacturing organizations should conduct ransomware preparedness assessments focusing on production system resilience, implement network segmentation isolating production systems from corporate networks, deploy industrial control system security monitoring, maintain offline backups of critical production configurations with regular restoration testing, review business continuity plans for extended production outages, audit supply chain dependencies and customer notification procedures, consider cyber insurance coverage for operational technology disruptions, and implement enhanced monitoring for lateral movement from IT to OT networks.
10. Gentlemen Ransomware Multi-Sector Campaign with Signed Driver Abuse
Gentlemen ransomware group launched sophisticated campaign in August 2025 demonstrating exceptionally tailored attack methodology across healthcare, financial services, manufacturing, and construction sectors globally.¹³ Attackers exploited vulnerable signed drivers to disable protection software, manipulated Group Policy Objects for lateral movement, and deployed custom anti-AV tools. Campaign featured privilege escalation, domain-level account compromise, and encrypted channel data exfiltration with victims concentrated in Thailand, United States, and APAC region. Attackers demonstrated advanced reconnaissance and persistence while shifting tactics mid-campaign, abusing legitimate tools (PowerRun.exe, PsExec) and domain-wide deployment via NETLOGON shares. Context-aware methods include targeting AnyDesk, Fortinet FortiGate, VMware ESXi, and Windows environments.¹³
Analyst Comment: Signed driver exploitation for security tool disablement demonstrates sophisticated understanding of Windows security architecture and willingness to invest in certificate acquisition or driver vulnerability research. Group Policy Object manipulation for lateral movement indicates domain administrator-level compromise enabling domain-wide malware deployment. Organizations must restrict execution of signed driver loading to authorized processes only, monitor for Group Policy Object modifications from non-administrative sources, implement application whitelisting for PowerRun.exe and PsExec usage, audit NETLOGON share permissions and monitor for unauthorized file placement, deploy EDR with anti-AV tool detection capabilities, segment networks to limit NETLOGON-based lateral movement, and review domain admin account usage patterns for anomalies.
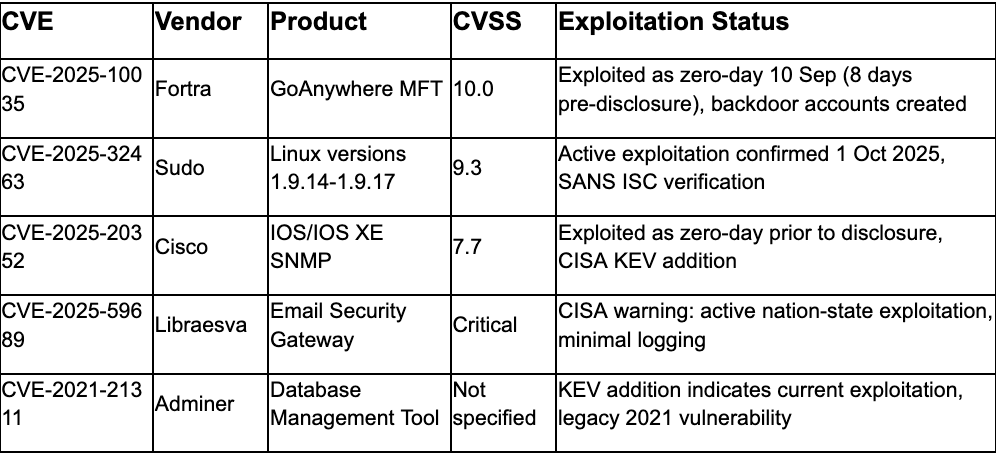
11. Fortra GoAnywhere MFT: CVSS 10.0 Zero-Day Exploited 8 Days Before Disclosure
watchTowr Labs provides credible evidence of active exploitation of CVE-2025-10035 in Fortra GoAnywhere Managed File Transfer software as early as September 10, 2025, one week before public disclosure on September 18.¹⁴ Vulnerability represents chain of three separate issues: access control bypass known since 2023, unsafe deserialization vulnerability CVE-2025-10035, and unknown private key issue. Exploitation enables creation of backdoor account "admin-go" followed by web user creation and deployment of additional payloads including SimpleHelp and zato_be.exe implant. Attack activity originated from IP address 155.2.190.197 previously flagged for brute-force attacks targeting Fortinet FortiGate SSL VPN appliances in August 2025. Fortra released version 7.8.4 or Sustain Release 7.6.3 to remediate, with CISA adding to KEV catalog requiring federal remediation by October 20, 2025.¹⁴
Analyst Comment: Eight-day exploitation window before public disclosure demonstrates threat actor access to vulnerability information through independent discovery or insider knowledge. The long history of GoAnywhere exploitation by APT groups and ransomware operators combined with CVSS 10.0 severity makes this flaw particularly dangerous for organizations operating managed file transfer infrastructure. Organizations must apply Fortra GoAnywhere updates to version 7.8.4 or 7.6.3 immediately, hunt for unauthorized user accounts named "admin-go" or similar variations, review GoAnywhere access logs for suspicious authentication patterns starting September 10, 2025, monitor for SimpleHelp and zato_be.exe indicators, restrict GoAnywhere MFT access to internal networks only, conduct compromise assessments on all GoAnywhere deployments, block IP address 155.2.190.197, review web user creation activities, and implement network segmentation isolating file transfer systems.
12. UNC5174 Exploits VMware Zero-Day Since October 2024
NVISO Labs disclosed newly patched security flaw CVE-2025-41244 (CVSS 7.8) impacting Broadcom VMware Tools and VMware Aria Operations exploited in wild as zero-day since mid-October 2024 by threat actor UNC5174.¹⁵ Local privilege escalation bug affecting VMware Cloud Foundation, vSphere Foundation, Aria Operations, VMware Tools, and Telco Cloud Platform enables malicious local actor with non-administrative privileges having access to VM with VMware Tools installed and managed by Aria Operations with SDMP enabled to escalate privileges to root on same VM. NVISO researcher Maxime Thiebaut credited for discovering and reporting shortcoming May 19, 2025 during incident response engagement. While Broadcom makes no mention of real-world exploitation, NVISO Labs attributed activity to China-linked threat actor Google Mandiant tracks as UNC5174 also known as Uteus or Uetus having track record of exploiting various security flaws including those impacting Ivanti and SAP NetWeaver.¹⁵
Vulnerability rooted in function get_version taking regular expression pattern as input for each process with listening socket checking whether binary associated with process matches pattern and if so invoking supported service's version command. Usage of broad-matching \S character class matching non-whitespace characters in several regex patterns also matches non-system binaries such as /tmp/httpd located within directories writable to unprivileged users by design. Opens door to potential abuse by unprivileged local attacker staging malicious binary at /tmp/httpd resulting in privilege escalation when VMware metrics collection executed. UNC5174 observed using /tmp/httpd location to stage malicious binary and spawn elevated root shell achieving code execution.¹⁵
Analyst Comment: Eleven-month exploitation window from October 2024 discovery to September 2025 disclosure represents extended opportunity for UNC5174 to compromise VMware infrastructure globally. The targeting of VMware management tools indicates focus on privileged access to virtualization infrastructure enabling lateral movement across virtual machine estates. Organizations must apply VMware security updates for CVE-2025-41244 immediately across all affected products, update VMware Tools to version 12.5.4 or later, monitor for suspicious binaries in /tmp directory mimicking system process names, detect privilege escalation attempts via VMware metrics collection processes, hunt for /tmp/httpd binary creation and execution, review VMware Aria Operations configurations for SDMP enablement, implement file integrity monitoring on temporary directories, audit listening sockets for non-system binary associations, deploy EDR solutions detecting UNC5174 TTPs, and restrict write permissions on temporary directories where feasible.
13. Motility Software Ransomware Affects 766,670 Individuals
Motility Software Solutions, provider of software for recreational vehicle and power sport dealers, disclosed ransomware attack discovered August 19, 2025.¹⁶ Attackers deployed file-encrypting ransomware on business operation servers while exfiltrating customer personal information files. Compromised data includes names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, dates of birth, Social Security numbers, and driver's license numbers affecting 766,670 individuals. Pear ransomware gang listed parent company Reynolds and Reynolds on Tor-based leak site claiming theft of 4.3 terabytes of data. Cybercrime group made data available for download suggesting no ransom paid. Company restored systems from clean backups and implemented additional security measures.¹⁶
Analyst Comment: Dealership software users should audit third-party vendor security postures, implement enhanced monitoring for ransomware targeting dealer management systems, review backup procedures ensuring offline copies with regular restoration testing, monitor for identity theft using compromised SSN and driver's license data, deploy network segmentation isolating dealer management platforms, implement enhanced access controls for systems containing customer PII, and verify security configurations across software-as-a-service providers.
14. Stellantis Data Breach via Salesforce Third-Party Compromise
Stellantis automotive manufacturer suffered data breach exposing North American customer contact information after attackers accessed third-party platform tied to Salesforce environment.⁴² ShinyHunters threat actor claims responsibility for stealing over 18 million Salesforce records. Stellantis owns Citroën, FIAT, Jeep, Chrysler, and Peugeot brands. Attack demonstrates continued targeting of Salesforce environments by sophisticated threat actors exploiting third-party integrations with OAuth token abuse enabling bulk data extraction from connected applications.⁴²
Analyst Comment: Salesforce customers should audit third-party platform integrations and OAuth permissions, review access logs for unauthorized API usage, implement enhanced monitoring for bulk data extraction, verify security configurations across connected applications, and conduct vendor security assessments for all Salesforce-integrated platforms.
15. Lotte Card Data Breach Exposes 3 Million South Korean Customers
South Korea's fifth-largest card issuer Lotte Card experienced data breach exposing personal information of approximately 3 million customers including identification numbers, contact details, card numbers, and verification codes.⁴³ Breach affected approximately 2,700 files with only 56% encrypted, creating immediate fraud risk. Incident linked to unpatched flaw on payment server with compromised data including sufficient information for fraudulent transactions.⁴³
Analyst Comment: Payment card issuers should conduct immediate vulnerability assessments on payment processing infrastructure, implement encryption for all customer data at rest, deploy intrusion detection on payment servers, review patch management processes for critical financial systems, monitor for fraudulent transactions using compromised data, and notify affected customers and card networks. The 56% encryption rate indicates inadequate data protection controls requiring immediate remediation.
16. Kido UK Nursery Chain Ransomware Targets Children's Data
UK nursery chain Kido with 18 sites in London and abroad was compromised by Radiant ransomware group.⁴⁴ Attackers stole data on approximately 8,000 children and employees including names, photos, addresses, contact details, and safeguarding notes. Radiant published profiles of 10 children online as proof while demanding ransom. Metropolitan Police and UK data regulators investigating with no arrests made and further leaks remaining possible. Attack targeting children's data represents heightened ethical and legal concerns with safeguarding notes potentially revealing child protection concerns and vulnerable family circumstances.⁴⁴
Analyst Comment: Childcare organizations should implement enhanced data protection for minor records, conduct risk assessments on data storage and access controls, deploy DLP solutions to prevent bulk data exfiltration, train staff on ransomware awareness, engage law enforcement immediately if children's data compromised, and review cyber insurance coverage for ransomware scenarios involving protected categories of individuals.
17. Grafana CVE-2021-43798 Coordinated Exploitation Campaign
On 28 September 2025, GreyNoise detected coordinated exploitation against Grafana path traversal vulnerability CVE-2021-43798 involving 110 unique malicious IP addresses, with 107 sourced from Bangladesh targeting U.S. endpoints.⁴⁵ Attackers used traversal payloads to access system files and Grafana configuration data containing credentials. Traffic analysis revealed uniform geographic targeting (3:1:1 ratio for US:Slovakia:Taiwan) and convergent tooling fingerprints indicating centralized orchestration. Two China-hosted IPs (60.186.152.35, 122.231.163.197) conducted focused probes exclusively on 28 September suggesting coordination with broader Bangladesh-sourced campaign.⁴⁵
Analyst Comment: The coordinated nature of 110 malicious IPs conducting synchronized exploitation against four-year-old Grafana vulnerability demonstrates organized campaign rather than opportunistic scanning. Organizations must update all Grafana instances to latest secure releases, audit web server logs for path traversal attempts dating to 28 September, block 110 identified malicious IPs, implement dynamic IP blocklists with JA3/JA4 signature support, and monitor for unauthorized file access in Grafana directories.
ACTIVE THREAT ACTORS
APT35 (Iranian): CVE-2023-23397 Credential Harvesting Campaign
Iranian-aligned APT35 launched credential-stealing campaign beginning early 2025 targeting government and military organizations worldwide.¹⁷ Initial vector exploits CVE-2023-23397 in Microsoft Outlook to bypass security models via weaponized Office documents. PowerShell stagers download primary credential-stealer modules from C2 servers. Malware hooks Windows Security Support Provider Interface (SSPI) to intercept NTLM challenge-response exchanges, capturing hashed credentials in memory. Stormshield documented compromise of defense ministry network in April 2025. Attackers employ hash-cracking and pass-the-hash techniques to unlock privileged accounts. Malware masquerades as legitimate processes and performs HTTP GET requests to C2 over port 443.¹⁷
LAPSUS$ / Scattered Spider / ShinyHunters Coordinated Operations
Resecurity analysis reveals significant operational connections between LAPSUS$, Scattered Spider, and ShinyHunters cybercrime groups since 2023.¹⁸ Telegram channel in August 2025 combined all three group brands for coordinating threats and marketing "shinysp1d3r" ransomware-as-a-service. Operational division confirmed: Scattered Spider provides initial access, ShinyHunters handles data exfiltration, LAPSUS$ participates in high-profile campaigns including Salesforce and Snowflake breaches. Groups employ sophisticated social engineering including SIM swapping, MFA bombing ("push fatigue"), vishing operations, and help desk impersonation. OAuth token abuse in Salesforce environments demonstrated by ShinyHunters' claims of stealing 1.5 billion records from 760 companies. Infostealers (Azorult, Lumma, RedLine, Raccoon, Vidar) harvest session cookies enabling authentication bypass.¹⁸
Confucius APT: AnonDoor Python Backdoor Campaign
Confucius hacker group active since 2013 escalated operations weaponizing malicious Office documents to compromise Windows endpoints with Python-based backdoor AnonDoor.¹⁹ Group historically deployed document stealers (WooperStealer) but shifted to sophisticated multi-stage infection chain leveraging OLE-embedded scripts, VBScript droppers, PowerShell loaders, and scheduled tasks for persistence. Fortinet identified initial access via spear-phishing with corrupted PPSX or DOCX attachments targeting South Asian government and defense organizations. When opened, documents display "Corrupted Page" concealing embedded OLE object triggering background fetch of secondary document from remote server. CMD stub initiates VBScript dropper marking first AnonDoor deployment. VBScript creates MSXML2.XMLHTTP object downloading raw DLL payload writing to %LocalAppData%\Mapistub.dll then staging execution via DLL side-loading.¹⁹
Patchwork APT: Scheduled Task Persistence Evolution
Patchwork APT resurgence since mid-2025 targets government and telecommunications organizations using evolved multi-stage infection chains.²⁰ Spear-phishing delivers malicious Office documents with weaponized macros triggering PowerShell scripts. K7 Security Labs identified enhanced persistence via dynamic URL generation and randomized scheduled task names. Malware employs multi-URL failover mechanism across compromised web servers. PowerShell creates scheduled tasks with names resembling Windows services executing at 30-minute intervals. Scripts use Invoke-Expression to stream payloads directly into memory from remote C2 servers. Final payload deploys custom backdoors enabling credential harvesting and lateral movement in government and telecommunications sectors across Asia and Eastern Europe.²⁰
Subtle Snail (UNC1549): Long-Term European Aerospace Espionage
Iran-linked Subtle Snail (UNC1549) espionage cell aligned with Charming Kitten has infiltrated 34 devices across 11 organizations since June 2022 with concerted shift toward European telecom, aerospace, and defense sectors.²¹ Modus operandi includes LinkedIn recruiting lures targeting employees to deploy MINIBIKE backdoor relaying via Azure-proxied C2 infrastructure cloaking malicious activity. Attackers use spearphishing, DLL sideloading, and signed binaries to deliver custom modules including keyloggers, browsers, and credential stealers. Group pursues long-term persistence through credential harvesting, sensitive file exfiltration, and lateral movement enabling sustained espionage against critical infrastructure and strategic industrial targets across Europe.²¹
Phantom Taurus: Newly Confirmed China Espionage Group
Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 identified newly confirmed China espionage group Phantom Taurus hitting almost 10 geopolitically important victims using extreme stealth.²² Uses distinct homegrown malware and backdoors. Infiltrated ministries of foreign affairs, embassies, diplomats, telecommunications networks stealing sensitive data around major summits and political events across Middle East, Africa, and Asia. Seeks sustained access with one case involving two-year access. Uses NET-STAR malware suite with three distinct web-based backdoors supporting in-memory execution of command-line arguments, arbitrary commands, payloads, and .NET payload loading with evasive capabilities. Most often exploits internet-facing devices via known vulnerabilities.²²
Chinese Nexus APT: NET-STAR Malware Targeting Finance and Telecommunications
Chinese Nexus APT conducting targeted campaigns using NET-STAR malware suite against finance, telecommunications, and manufacturing sectors globally.²³ Attackers employ spear-phishing with weaponized industry whitepapers and compromised VPN credentials for initial access with success rate approximately 30% against high-value targets. Infection leverages living-off-the-land techniques with PowerShell executing obfuscated scripts in memory. Palo Alto Networks identified initial stager decoding Base64 .NET binaries and injecting into explorer.exe or svchost.exe. NET-STAR features modular design with loader, backdoor, and C2 communication components. C2 module uses encrypted HTTPS tunnel with custom framing protocol and 256-bit AES encryption. Campaign objectives include intellectual property theft and positioning for future sabotage operations.²³
SideWinder APT: Fake Webmail Portal Credential Harvesting
APT SideWinder launched mid-2025 campaign using fake Outlook and Zimbra login portals hosted on Netlify, pages.dev, and workers.dev platforms.²⁴ Operation employs maritime and defense-themed lure documents targeting government personnel in Pakistan, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, and Myanmar. Hunt.io observed rapid domain churn with new phishing sites every 3-5 days beginning August 2025. Portals capture credentials via direct POST requests to attacker-controlled endpoints. Sites impersonate Bangladesh's Directorate General of Defense Purchases and Nepal's Ministry of Finance. JavaScript obfuscation includes Base64 encoding and staged redirections. Harvested credentials enable network access and subsequent malware deployment.²⁴
Nimbus Manticore (Iranian): European Defense and Telecommunications Targeting
Check Point Research uncovered campaign by Iranian threat actor Nimbus Manticore targeting European defense and telecommunications sectors.²⁵ Group employs spear-phishing and fake HR portals to deploy DLL side-loading chain with obfuscated malware including MiniJunk and MiniBrowse. Tools employ valid code signatures and advanced evasion techniques indicating nation-state capabilities. Campaign demonstrates continued Iranian cyber espionage against European critical infrastructure.²⁵
China PlugX Variant: Central and South Asian Telecommunications Campaign
Cisco Talos identified ongoing campaign distributing new PlugX variant targeting telecommunications and manufacturing sectors in Central and South Asian countries.²⁶ New variant's features overlap with both RainyDay and Turian backdoors including abuse of legitimate applications for DLL side-loading and XOR-RC4-RtlDecompressBuffer encryption algorithm. Configuration adopts same structure used in RainyDay backdoor associated with China-linked Lotus Panda. Attack chains abuse legitimate Mobile Popup Application executable to sideload malicious DLL launching PlugX, RainyDay, and Turian payloads in memory. Recent attacks include embedded keylogger plugin targeting telecommunications firm in Kazakhstan.²⁶
Mustang Panda: Bookworm Malware ASEAN Campaign
Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 detailed Bookworm malware used by Mustang Panda actor since 2015 for extensive system control.²⁷ Advanced RAT with capabilities to execute arbitrary commands, upload/download files, exfiltrate data, and establish persistent access. March 2025 attacks targeted Association of Southeast Asian Nations countries. Bookworm utilizes legitimate-looking domains for C2 purposes blending with normal traffic. Newer variants package shellcode as UUID strings which are decoded and executed. Known for unique modular architecture loading additional modules directly from C2 server.²⁷
CountLoader: Multi-Form Malware with Ransomware Group Integration
Sophisticated CountLoader malware operates in three forms (.NET, PowerShell, JScript) implicated in campaigns tied to LockBit, BlackBasta, and Qilin ransomware groups.²⁸ Loader distributed via phishing lures masquerading as Ukrainian police documents leveraging domain-joined environments for initial access. CountLoader stages payloads including Cobalt Strike, AdaptixC2, PureHVNC, and Lumma Stealer through multiple techniques tailored for corporate networks. Malware utilizes persistence via scheduled tasks and registry modifications while dynamically communicating with evolving C2 infrastructure across dozens of domains. Campaign demonstrates advanced understanding of domain-joined Windows environments and Active Directory exploitation.²⁸
FunkSec Group: AI-Powered FunkLocker Ransomware
FunkSec group deployed AI-powered FunkLocker ransomware demonstrating AI-assisted malware development following "Ask AI → Paste snippet" model resulting in inconsistent code quality with some builds barely functional while others incorporate advanced anti-VM checks.²⁹ Upon execution ransomware aggressively terminates predefined processes and services using taskkill.exe and sc.exe targeting security tools including Windows Defender, Windows Firewall, and Shell Experience Host causing victim screen blackout. Heavily abuses PowerShell to disable real-time monitoring, clear security and application event logs using wevtutil, and bypass execution policy. Uses vssadmin.exe to delete all shadow volume copies preventing system recovery. Encryption performed entirely locally without C2 communication with files encrypted using .funksec extension and ransom note dropped to desktop. Poor operational security includes Bitcoin wallet address reuse across victims and hardcoded or locally-derived encryption keys enabling Avast Labs to release public decryptor. Group maintains data leak site publicizing stolen information with significant victim concentration in United States plus incidents reported in India, Spain, Mongolia affecting government, defense, technology, and finance sectors with 120+ victims claimed since late 2024.²⁹
EvilAI Campaign: AI Tool Masquerade with Legitimate Binary Signing
EvilAI global malware campaign identified targeting organizations across Europe, Americas, and AMEA regions masquerading as legitimate productivity and AI tools using polished interfaces and legitimately signed binaries to bypass scrutiny.³⁰ Attackers employ convincing functionality via deceptive installers and social engineering for initial access. Campaign exfiltrates browser credentials from Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, establishes persistence through scheduled tasks and registry modifications, and maintains AES-encrypted C2 channels. Malware executes remote commands, deploys additional payloads, and deliberately obfuscates activity using AI-generated code and dynamic behavior to frustrate detection. Targets include IT, healthcare, financial services, manufacturing, construction, government, education, retail, and distributor sectors.³⁰
TRENDS
Five Eyes Coordination Demonstrates Maturation of Threat Intelligence Sharing
CISA Emergency Directive 25-03 triggered coordinated response across Five Eyes partners within 24 hours of U.S. federal directive with synchronized vulnerability disclosure, threat attribution, and remediation guidance.²'³¹'³² Canadian Centre for Cyber Security issued Alert AL25-012 on 26 September characterizing Cisco vulnerabilities as "serious and urgent" urging all critical infrastructure sectors including municipal, provincial, and territorial governments to act swiftly.³¹ Australian Signals Directorate's Australian Cyber Security Centre issued Critical-rated alert on 26 September confirming awareness of targeting within Australia.³² UK National Cyber Security Centre released malware analysis for RayInitiator and LINE VIPER implants associated with ArcaneDoor campaign documenting ROM modification techniques.² The synchronized response represents formalized procedures for responding to critical infrastructure threats with clear evidence that ROM-level persistence capabilities in network perimeter devices represent strategic threat requiring immediate multinational response.
Analyst Comment: Unprecedented coordination among Five Eyes nations within 24-48 hours of vulnerability disclosure indicates evolution from ad-hoc information sharing to formalized coordinated disclosure and response procedures. The consistency of messaging across five national cybersecurity agencies (CISA, UK NCSC, Canadian CCCS, Australian ACSC) regarding threat severity, attribution confidence, and remediation urgency demonstrates effective threat intelligence sharing mechanisms. Organizations operating in Five Eyes countries should expect similar coordinated responses for future critical infrastructure compromises and can leverage parallel advisories from multiple national authorities to justify emergency patching budgets and change control exceptions.
Legacy Vulnerability Exploitation Surge Indicates Systematic Targeting
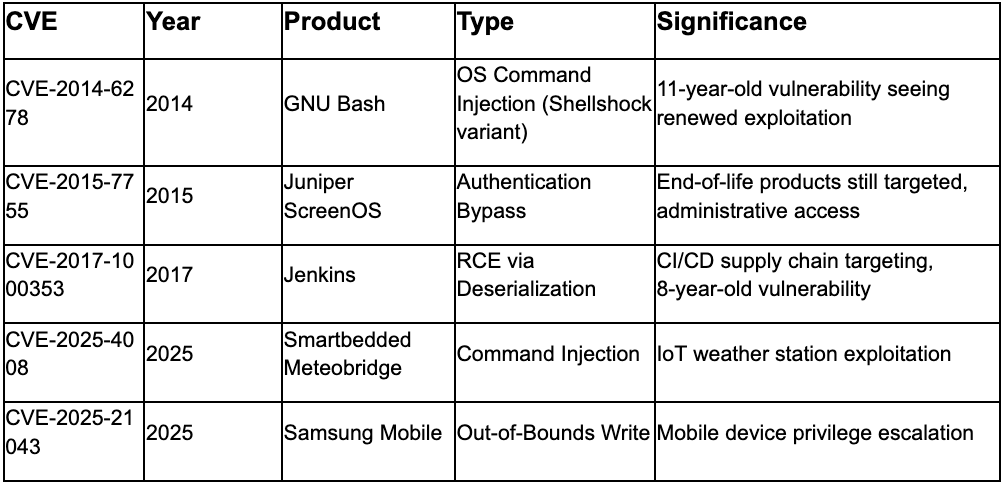
CISA added ten vulnerabilities to Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog during collection period, with five additions on 2 October consisting entirely of legacy vulnerabilities dating from 2014-2017.³³ CVE-2014-6278 (GNU Bash Shellshock variant), CVE-2015-7755 (Juniper ScreenOS authentication bypass), CVE-2017-1000353 (Jenkins RCE deserialization), CVE-2025-4008 (Smartbedded Meteobridge command injection), and CVE-2025-21043 (Samsung Mobile out-of-bounds write) represent pattern of adversaries exploiting unpatched legacy systems in current campaigns. SANS Internet Storm Center honeypot analysis confirmed persistent exploitation of IoT devices using predictable cookie-based authentication mechanisms including CVE-2024-37721 (TBK DVR command injection), CVE-2023-26801 (LB-LINK router vulnerability), and Tenda O3V2 wireless access point OS injection targeting wireless internet service providers.³⁴ Analysis reveals IoT devices with weak authentication mechanisms remain under active exploitation despite vulnerability age.
Analyst Comment: Inclusion of multiple legacy vulnerabilities (2014-2017 CVEs) in October KEV additions suggests adversaries systematically targeting unpatched legacy systems as organizations focus patching resources on recent disclosures. The pattern indicates threat actors maintaining exploit databases spanning decade-old vulnerabilities and conducting internet-wide scanning for vulnerable legacy infrastructure, particularly targeting IoT devices and end-of-life products no longer receiving vendor security updates. Organizations must extend vulnerability management programs to include legacy and end-of-life systems, implement network segmentation isolating legacy infrastructure from production networks, accelerate hardware refresh cycles for systems beyond vendor support windows, deploy compensating controls where patching impossible, and consider legacy system risk in cybersecurity insurance assessments.
Supply Chain Attacks Demonstrate Coordinated Developer Ecosystem Targeting
Three major supply chain compromises occurred within seven-day collection period targeting npm ecosystem (@ctrl/tinycolor affecting 2.2 million weekly downloads, CrowdStrike-maintained packages), PyPI repository (SilentSync RAT via termncolor/sisaws/secmeasure typosquatting), and Model Context Protocol (postmark-mcp first-ever malicious MCP server).⁵'³⁵'³⁶ npm attack demonstrated sophisticated evolution through seven bundle.js variants (v1-v7) refining credential harvesting tactics, validating npm tokens via whoami endpoint, and integrating with GitHub APIs for systematic data theft. PyPI campaign employed typosquatting with packages containing initialization code decoding hex strings revealing curl commands downloading helper Python scripts from Pastebin, with SilentSync RAT supporting remote command execution, file exfiltration, screenshot capture, and browser data theft from Chromium-based browsers and Firefox. MCP attack represented first-ever instance of malicious Model Context Protocol server with developer slipping rogue code within npm package postmark-mcp copying official Postmark Labs library, attracting 1,643 downloads before removal, with malicious functionality introduced in version 1.0.16 quietly forwarding every email to developer's personal server.³⁶
Analyst Comment: Concentration of three distinct supply chain attacks within single week across multiple package ecosystems (npm, PyPI, MCP) indicates either coordinated campaign or multiple threat actors simultaneously recognizing developer supply chains as high-value targets with low detection rates. Common tactics include typosquatting established packages, evolving malware through multiple variants to refine detection evasion, automatic execution upon installation, and targeting of security vendor packages for elevated access to downstream customers. Organizations must implement supply chain security scanning for all package managers, audit package dependencies for malicious versions, rotate credentials potentially exposed to compromised packages, verify package authenticity through official vendor channels only, implement code review processes for all third-party dependencies, deploy behavioral analysis detecting credential harvesting attempts, and maintain software bill of materials enabling rapid identification of compromised components during disclosure events.
MS-ISAC Federal Funding Termination Creates SLTT Infrastructure Gap
CISA's cooperative agreement with Center for Internet Security terminated effective 30 September 2025, ending $27 million annual federal funding for MS-ISAC operations serving 18,000+ U.S. state, local, tribal, and territorial government organizations as primary cybersecurity resource and threat intelligence hub.³⁷ Services affected include 24x7x365 Security Operations Center, Albert intrusion detection sensors, Malicious Domain Blocking and Reporting (MDBR), and annual National Cybersecurity Self-Assessment programs. CIS implementing fee-based membership model for core services with limited disruptions expected during transition period. CISA announced alternative support through State and Local Cybersecurity Grant Program, free vulnerability scanning tools, and regional cybersecurity advisors. Timing coincides with potential federal government shutdown and expiration of Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act of 2025. This represents second major ISAC funding cut in 2025 following February termination of Elections Infrastructure ISAC (EI-ISAC) support.³⁷
Analyst Comment: This funding termination creates immediate operational gaps for thousands of SLTT entities that relied on MS-ISAC for threat intelligence, incident response, and security monitoring capabilities. The transition to fee-based model during period of heightened cyber threats against critical infrastructure poses significant risks to smaller jurisdictions with limited cybersecurity budgets. Available evidence suggests this will reduce real-time threat sharing and coordinated response capabilities across SLTT community at time when ArcaneDoor, Salt Typhoon, and other nation-state campaigns actively target state and local government infrastructure. SLTT organizations must evaluate alternative threat intelligence sources, assess budget allocation for MS-ISAC fee-based services, engage with CISA regional cybersecurity advisors, pursue State and Local Cybersecurity Grant Program funding, and strengthen peer-to-peer threat intelligence sharing through sector-specific ISACs and regional partnerships.
Quantum Computing Timeline Establishes 2030 as Critical Cryptography Transition Milestone
FS-ISAC released white paper "The Timeline for Post Quantum Cryptographic Migration" establishing coordinated global transition framework for financial sector identifying 2030-2031 as critical transition point when NIST and international authorities will deprecate quantum-vulnerable algorithms including RSA-2048.³⁸ Report warns "harvest now, decrypt later" attack model poses immediate risks as threat actors collect encrypted data for future quantum computer decryption, with financial sector facing sector-wide coordination requirements due to interconnectedness and shared vendor dependencies. FS-ISAC emphasizes post-quantum cryptography transition is collaborative project rather than competitive initiative requiring institutions to identify all cryptographic systems, assess quantum vulnerability, and develop comprehensive migration roadmaps. Report warns of "crypto-procrastination" among financial institutions underestimating migration complexity and misunderstanding quantum threat urgency.³⁸
Analyst Comment: Current intelligence indicates financial sector faces compressed timeline for quantum-resistant cryptography adoption with multiple indicators pointing to inadequate preparation across sector. The interconnected nature of financial systems means delayed migration by any major institution creates systemic vulnerabilities affecting transaction processing, secure communications, and regulatory compliance. Analysis suggests institutions must begin immediate cryptographic inventory and migration planning to meet 2030 deadline given typical multi-year timelines for enterprise cryptographic system replacements. Organizations should prioritize identifying systems with long data retention requirements, assess quantum vulnerability of current cryptographic implementations, engage with NIST post-quantum cryptography standardization process, begin vendor discussions on quantum-resistant product roadmaps, and allocate budget and resources for multi-year migration programs.
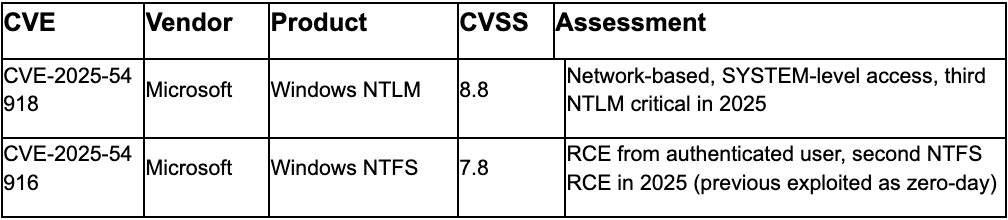
Windows NTLM Vulnerability Recurrence Pattern Indicates Sustained Targeting
Microsoft September 2025 Patch Tuesday addressed CVE-2025-54918, marking the third critical NTLM elevation of privilege vulnerability in 2025 following CVE-2025-53778 in August and CVE-2025-21311 in January.⁴⁶ CVE-2025-54918 rated with "Exploitation More Likely" assessment enables network-based attackers to achieve SYSTEM-level privileges through specially crafted packets despite classification as privilege escalation rather than remote code execution. The recurrence pattern demonstrates sustained threat actor interest in Windows authentication infrastructure with NTLM representing attractive target due to widespread enterprise deployment and privilege escalation potential. Tenable analysis highlights that all three 2025 NTLM vulnerabilities share similar exploitation characteristics enabling remote attackers to escalate privileges through authentication protocol weaknesses.⁴⁶
Analyst Comment: The pattern of three critical NTLM vulnerabilities within nine months indicates either sustained threat actor research focus on Windows authentication protocols or Microsoft discovery of related vulnerability class requiring systematic remediation. Organizations must prioritize deployment of all three NTLM patches, implement enhanced monitoring for NTLM authentication anomalies, consider migration strategies toward Kerberos authentication where feasible, deploy credential guard and LSASS protection, enable advanced logging for authentication events, and review network segmentation limiting NTLM relay attack surface. The "Exploitation More Likely" rating on latest NTLM vulnerability combined with historical pattern suggests imminent exploitation attempts once technical details become available.
VULNERABILITIES
Critical Patches Required This Month (October 2025)
Federal Deadline: 20 October 2025 (CISA KEV - 29 September Additions)
Immediate Patching Required (No Federal Deadline Specified)
September 2025 Patch Tuesday (High Priority)
"Exploitation More Likely" Vulnerabilities
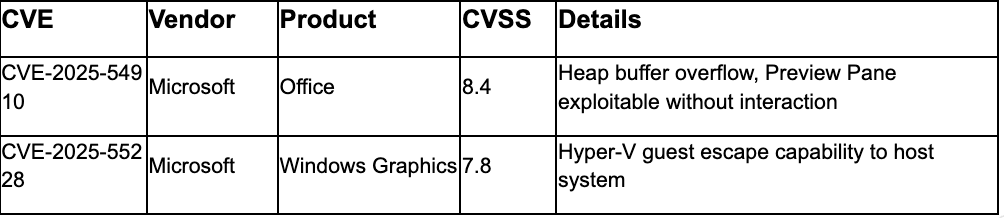
Critical Remote Code Execution
Legacy Vulnerabilities Added to CISA KEV (2 October 2025)
Pattern Analysis: Adversaries Targeting Unpatched Legacy Infrastructure
Oracle E-Business Suite (July 2025 CPU - Retroactive Priority)
Potentially Exploited in Cl0p Extortion Campaign
GOVERNMENT VICTORIES
UK Law Enforcement: Rapid Arrest in Collins Aerospace Ransomware Attack
UK authorities quickly arrested individuals in connection with ransomware attack against Collins Aerospace's MUSE check-in and boarding system that disrupted Brussels, Berlin, and London Heathrow airports causing widespread delays and cancellations.¹¹ ENISA confirmed ransomware with investigations continuing through days of residual disruption into September 23. The rapid law enforcement response suggests either domestic threat actors or strong international cooperation enabling swift attribution and apprehension.
Dutch Authorities: Arrests of Teenagers Assisting Russian Hackers
Dutch authorities arrested two 17-year-old boys September 2025 on suspicion of assisting pro-Russian hackers with government-sponsored interference activities.³⁹ Threat actors recruited teenagers via Telegram with one suspect allegedly carrying Wi-Fi sniffer near Europol headquarters, Eurojust headquarters, and Canadian embassy for network mapping and data interception. One teen placed on home bail with an ankle monitor while another remained in custody pending hearing within two weeks. A suspect in custody was arrested while doing homework with electronic equipment seized during search warrant execution. Similar incidents recently reported in Germany and Ukraine where Russian threat actors lured teenagers into performing vandalism against official buildings or filming government infrastructure.³⁹
Interpol Operation: 260 Arrests Across 14 African Countries for Romance Scams
Interpol-coordinated operation in July-August 2025 resulted in 260 arrests across 14 African countries for online romance and extortion scams.⁴⁰ Campaigns targeted over 1,400 victims resulting in nearly $2.8 million losses. Perpetrators built fake online romantic relationships to extract money or blackmail victims with explicit images. Ghanaian authorities arrested 68 suspects using fake identities to trick victims into paying fake shipment fees while secretly recording explicit videos for blackmail. Senegal arrested 22 suspects posing as celebrities on social media and dating platforms scamming over 100 people out of approximately $34,000. Ivory Coast arrested 24 suspects using fake profiles to obtain and blackmail victims with intimate images. Interpol reports sharp rise in digital-enabled crimes including sextortion and romance scams across Africa with growth of online platforms opening new opportunities for criminal networks causing both financial loss and psychological harm to victims.⁴⁰
U.S. Law Enforcement: Scattered Spider Suspect Prosecution Proceedings
17-year-old suspect surrendered over alleged role in 2023 cyberattacks against two major Las Vegas casino operators released to parents under strict supervision.⁴¹ Family Court Judge Dee Smart Butler ordered teen originally from Chicago area to remain in Clark County under parental supervision, barred from unsupervised internet access with cell phone and electronic device use strictly prohibited unless for approved academic purposes or when accompanied by parent. Prosecutors intent on trying as adult with determination revisited at the November hearing. Chief Deputy District Attorney Summer Clarke disclosed a suspect accused of orchestrating network intrusions resulting in millions of dollars damage including theft of sensitive data such as Social Security numbers. Between August and October 2023 MGM Resorts International suffered approximately $200 million damages while Caesars Entertainment reportedly paid $15 million ransomware settlement. Authorities believe the teen still controls roughly $1.8 million bitcoin acquired during attacks though current location remains unknown. FBI search warrants executed on the suspect's Illinois residence December 2023 and February 2025 yielded digital evidence linking to breaches. Metropolitan Police Department confirmed counts including obtaining or using personally identifying information, extortion, and unlawful computer-related acts.⁴¹
RECOMMENDATIONS
Immediate Actions (0-24 Hours)
CISA Emergency Directive Compliance: Organizations using Cisco ASA or Firepower devices must immediately complete CISA ED 25-03 requirements including device identification, memory core dump collection (if applicable), patch deployment, and complete inventory reporting. The federal deadline of 26 September has passed; late compliance required immediately. Over 48,800 internet-exposed devices remain vulnerable requiring urgent remediation. Organizations must prioritize forensic analysis on legacy ASA 5500-X series platforms lacking Secure Boot capabilities where ROM manipulation is most feasible.
KEV Remediation Before 20 October Federal Deadline: Apply patches for CVE-2025-10035 (Fortra GoAnywhere CVSS 10.0 exploited 8 days before disclosure), CVE-2025-32463 (Sudo privilege escalation CVSS 9.3), CVE-2025-20352 (Cisco IOS/IOS XE SNMP exploited as zero-day), CVE-2025-59689 (Libraesva ESG command injection with nation-state exploitation), and CVE-2021-21311 (Adminer SSRF legacy vulnerability). All five demonstrate confirmed active exploitation with federal agencies required to remediate by 20 October 2025.
Supply Chain Audit - npm Ecosystem: Immediately audit npm packages for @ctrl/tinycolor dependencies and malicious bundle.js variants (v1-v7). Organizations must rotate all npm tokens, GitHub credentials, and CI/CD secrets. Review GitHub Actions workflows for unauthorized modifications. Block identified exfiltration endpoints. Implement npm package integrity verification. Deploy supply chain security scanning. Monitor for TruffleHog credential scanning attempts. Audit CI/CD pipelines for compromised secrets. Specifically check for CrowdStrike-maintained packages affected by 500+ malicious package campaigns.
Red Hat Consulting Client Response: Organizations identified as Red Hat Consulting clients must immediately rotate all credentials, SSH keys, API tokens, and database connection strings. Review container deployment manifests for unauthorized changes. Implement additional monitoring on systems referenced in stolen infrastructure blueprints. Engage incident response teams for comprehensive forensic analysis. Hunt for usage of compromised authentication material in network logs dating to breach windows.
Oracle E-Business Suite Customers: Apply July 2025 Critical Patch Update immediately addressing CVE-2025-30746, CVE-2025-30745, CVE-2025-50107, CVE-2025-30743, CVE-2025-30744, CVE-2025-50105. Review access logs for unauthorized patterns since July 2025. Implement enhanced logging on E-Business Suite instances. Restrict E-Business Suite exposure to the internet. Hunt for unusual authentication patterns or data exfiltration. Monitor for extortion emails from compromised third-party accounts.
DrayTek Router Emergency Patching: Apply firmware updates immediately per DrayTek advisory DSA-2025-005 for CVE-2025-10547 affecting Vigor1000B, Vigor2962, Vigor3910, Vigor2135, and multiple series (276x, 286x, 291x, 292x, 295x). Disable WAN-side WebUI and SSL VPN access until patched. Implement ACLs to restrict management interface access. Segment LAN access using VLANs where possible. Hunt for unauthorized configuration changes on vulnerable devices.
VMware Infrastructure Assessment: Apply VMware security updates for CVE-2025-41244 immediately across VMware Tools, Aria Operations, Cloud Foundation, vSphere Foundation, and Telco Cloud Platform. Update VMware Tools to version 12.5.4 or later. Monitor for suspicious binaries in /tmp directory mimicking system process names (particularly /tmp/httpd). Hunt for privilege escalation attempts via VMware metrics collection processes. Review Aria Operations configurations for SDMP enablement.
Short-Term Actions (1-7 Days)
Phishing-Resistant MFA Migration: Migrate from SMS-based and one-time password MFA to phishing-resistant authentication methods including FIDO2 hardware tokens. SonicWall CVE-2024-40766 exploitation by Akira ransomware with hour-long dwell times demonstrates OTP-based MFA provides insufficient protection against sophisticated threat actors. Upgrade SonicOS to version 7.3 or later addressing brute-force vulnerabilities affecting MFA credentials. Monitor for VPN logins from VPS hosting provider ASNs. Implement behavioral monitoring distinguishing legitimate backup activity from malicious mimicry of Datto RMM or backup agent operations.
Comprehensive Threat Hunting Operations: Deploy hunting campaigns for multiple APT groups active during collection period including APT35 (SSPI hooking for NTLM credential theft via CVE-2023-23397), Salt Typhoon (Demodex rootkit targeting telecommunications lawful intercept systems), Patchwork APT (scheduled tasks executing every 30 minutes with randomized names), Confucius (AnonDoor Python backdoor via OLE object exploitation), Subtle Snail/UNC1549 (MINIBIKE backdoor with Azure-proxied C2), and Phantom Taurus (NET-STAR malware suite with in-memory .NET execution). Deploy behavioral analytics detecting memory-resident malware, DLL side-loading, in-memory payload execution, and unusual scheduled task creation patterns.
North Korean IT Worker Enhanced Screening: Implement comprehensive remote worker screening procedures including video interviews with unexpected technical questions testing claimed expertise, verify identity documents through multiple independent channels, monitor for proxy interviewing indicators including audio/video discrepancies or response delays suggesting off-camera assistance, implement behavioral analytics detecting unusual work patterns or productivity anomalies, review contractor vetting procedures extending beyond technology roles to finance and engineering positions, deploy endpoint detection hunting for BeaverTail, InvisibleFerret, Tropidoor, and AkdoorTea malware families, and train HR personnel on North Korean IT worker social engineering tactics and fake recruitment operations.
Critical Infrastructure Network Segmentation: Implement network segmentation isolating production systems from corporate networks, particularly for manufacturing environments following Asahi Group production suspension affecting 40% of Japan beer market. Deploy industrial control system security monitoring. Maintain offline backups of critical production configurations with regular restoration testing. Review business continuity plans for extended production outages. Audit supply chain dependencies and customer notification procedures. Consider cyber insurance coverage specifically addressing operational technology disruptions. Implement enhanced monitoring for lateral movement from IT to OT networks.
Third-Party Vendor Risk Assessment: Conduct comprehensive security assessments of HR service providers (reference: Volvo Group/Miljödata ransomware exposing employee SSNs), Salesforce platform integrations (reference: Stellantis breach via third-party Salesforce connection exposing 18M records), email security gateway deployments (reference: Libraesva CVE-2025-59689 nation-state exploitation), and consulting firm access (reference: Red Hat GitLab 570GB exposure). Audit third-party platform integrations and OAuth permissions. Verify security configurations across connected applications. Implement enhanced monitoring for unusual data access patterns in third-party integrated systems. Review contracts with service providers for incident response obligations and liability provisions.
Supply Chain Security Program Enhancement: Implement comprehensive supply chain security scanning across all package managers (npm, PyPI, RubyGems, Maven, NuGet). Audit package dependencies for typosquatting, malicious versions, and suspicious maintainer changes. Verify package authenticity through official vendor channels only. Implement code review processes for all third-party dependencies before production deployment. Deploy behavioral analysis detecting credential harvesting, unexpected network connections, or filesystem modifications during package installation. Maintain a software bill of materials enabling rapid identification of compromised components during disclosure events. Establish vendor security assessment requirements including supply chain security controls, software development lifecycle practices, and incident notification procedures.
Microsoft Patch Tuesday Priority Deployment: Prioritize deployment of September 2025 Patch Tuesday updates addressing CVE-2025-54918 (Windows NTLM EoP, third NTLM critical in 2025), CVE-2025-54916 (Windows NTFS RCE with "Exploitation More Likely" rating, second NTFS RCE in 2025 following zero-day exploitation of previous variant), CVE-2025-54910 (Microsoft Office RCE exploitable via Preview Pane without user interaction), CVE-2025-55228 (Windows Graphics Component RCE enabling Hyper-V guest escape), and CVE-2025-55234 (Windows SMB Server EoP publicly disclosed requiring SMB signing and Extended Protection for Authentication). Deploy appropriate mitigations where immediate patching is not feasible including SMB signing enforcement, EPA configuration, and Office Preview Pane restrictions.
Legacy System Risk Management: Extend vulnerability management programs to include legacy and end-of-life systems following CISA KEV additions of CVE-2014-6278 (GNU Bash Shellshock), CVE-2015-7755 (Juniper ScreenOS), and CVE-2017-1000353 (Jenkins) demonstrating adversary systematic targeting of decade-old vulnerabilities. Implement network segmentation isolating legacy infrastructure from production networks. Accelerate hardware refresh cycles for systems beyond vendor support windows. Deploy compensating controls where patching is impossible including restrictive firewall rules, enhanced monitoring, and privileged access management. Document legacy system risks in cybersecurity insurance assessments and risk registers.
References
- Check Point Research. (2025, September 29). 29th September – Threat intelligence report. https://research.checkpoint.com/2025/29th-september-threat-intelligence-report/
- Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency. (2025, September 25). Emergency Directive 25-03: Identify and mitigate potential compromise of Cisco devices. https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/directives/ed-25-03-identify-and-mitigate-potential-compromise-cisco-devices
- Rapid7. (2025, September 25). Multiple critical vulnerabilities affecting Cisco products | CVE-2025-20333, CVE-2025-20362, CVE-2025-20363. https://www.rapid7.com/blog/post/etr-cve-2025-20333-cve-2025-20362-cve-2025-20363-multiple-critical-vulnerabilities-affecting-cisco-products/
- Cybersecuritynews.com. (2025, October). Red Hat confirms data breach after hackers claim to steal 570GB of private GitHub repositories. https://cybersecuritynews.com/red-hat-confirms-data-breach/
- Cybersecuritynews.com. (2025, October). Threat actors compromising NPM ecosystem to steal developer credentials. https://cybersecuritynews.com/npm-supply-chain-attack/
- Kovacs, E. (2025, October 3). Oracle says known vulnerabilities possibly exploited in recent extortion attacks. SecurityWeek. https://www.securityweek.com/oracle-says-known-vulnerabilities-possibly-exploited-in-recent-extortion-attacks/
- Cybersecuritynews.com. (2025, October). Chinese state-sponsored hackers attacking telecommunications infrastructure to harvest sensitive data. https://cybersecuritynews.com/chinese-state-sponsored-hackers-attacking-telecommunications/
- Arghire, I. (2025, September 29). Akira ransomware's exploitation of SonicWall vulnerability continues. SecurityWeek. https://www.securityweek.com/akira-ransomwares-exploitation-of-sonicwall-vulnerability-continues/
- Arghire, I. (2025, September 26). North Korea's fake recruiters feed stolen data to IT workers. SecurityWeek. https://www.securityweek.com/north-koreas-fake-recruiters-feed-stolen-data-to-it-workers/
- SC Media. (2025, September 30). Cisco, Sudo, Fortra flaws added to CISA's known exploited vulnerabilities list. https://www.scworld.com/news/cisco-sudo-fortra-flaws-added-to-cisas-known-exploited-vulnerabilities-list\
- Cyberone. (2025, September 23). Weekly cybersecurity report | Week 39, 2025. https://cyberone.bg/en/weekly-cybersecurity-report-week-39-2025
- Arghire, I. (2025, September 30). Cyberattack on beer giant Asahi disrupts production. SecurityWeek. https://www.securityweek.com/cyberattack-on-beer-giant-asahi-disrupts-production/
- Tata Communications. (2025, September 30). Your weekly threat intelligence advisory. https://www.tatacommunications.com/hubfs/TaCO-2024/threat-advisory/doc/threat-intelligence-advisory-30-september-2025.pdf
- The Hacker News. (2025, September). Fortra GoAnywhere CVSS 10 flaw exploited as 0-day a week before public disclosure. https://thehackernews.com/2025/09/fortra-goanywhere-cvss-10-flaw.html
- The Hacker News. (2025, September). Urgent: China-linked hackers exploit new VMware zero-day since October 2024. https://thehackernews.com/2025/09/urgent-china-linked-hackers-exploit-new.html
- Arghire, I. (2025, October 2). 766,000 impacted by data breach at dealership software provider Motility. SecurityWeek. https://www.securityweek.com/766000-impacted-by-data-breach-at-dealership-software-provider-motility/
- Cybersecuritynews.com. (2025, October). APT35 hackers attacking government, military organizations to steal login credentials. https://cybersecuritynews.com/apt35-hackers-attacking-government-military-organizations/
- Cybersecuritynews.com. (2025, October). Researchers uncovered connections between LAPSUS$, Scattered Spider, and ShinyHunters hacker groups. https://cybersecuritynews.com/researchers-uncovered-connections-between-lapsus-scattered-spider/
- Cybersecuritynews.com. (2025, October). Confucius hacker group attacking weaponizing documents to compromised Windows systems with AnonDoor malware. https://cybersecuritynews.com/confucius-hacker-group-attacking-weaponizing-documents/
- Cybersecuritynews.com. (2025, October). Patchwork APT using PowerShell commands to create scheduled task and downloads final payload. https://cybersecuritynews.com/patchwork-apt-using-powershell-commands/
- Cybersecuritynews.com. (2025, October). Iran-linked espionage campaign targets European aerospace and defense sectors. https://cybersecuritynews.com/iran-linked-espionage-europe/
- CyberScoop. (2025, September). Palo Alto Networks spots new China espionage group showcasing advanced skills. https://cyberscoop.com/phantom-taurus-china-espionage-group/
- Cybersecuritynews.com. (2025, October). New Chinese nexus APT hackers attacking organizations to deliver NET-STAR malware suite. https://cybersecuritynews.com/new-chinese-nexus-apt-hackers-attacking-organizations/
- Cybersecuritynews.com. (2025, October). SideWinder hacker group hosting fake Outlook/Zimbra portals to steal login credentials. https://cybersecuritynews.com/sidewinder-hacker-group-hosting-fake-outlook-portals/
- Check Point Research. (2025, September 29). 29th September – Threat intelligence report - Vulnerabilities and patches section. https://research.checkpoint.com/2025/29th-september-threat-intelligence-report/
- The Hacker News. (2025, September). China-linked PlugX and Bookworm malware attacks target Asian telecom and ASEAN networks. https://thehackernews.com/2025/09/china-linked-plugx-and-bookworm-malware.html
- The Hacker News. (2025, September). China-linked PlugX and Bookworm malware attacks target Asian telecom and ASEAN networks. https://thehackernews.com/2025/09/china-linked-plugx-and-bookworm-malware.html
- Tata Communications. (2025, September 30). Your weekly threat intelligence advisory. https://www.tatacommunications.com/hubfs/TaCO-2024/threat-advisory/doc/threat-intelligence-advisory-30-september-2025.pdf
- Cybersecuritynews.com. (2025, October). AI-powered FunkLocker ransomware leverages Windows utilities to disable defenses. https://cybersecuritynews.com/ai-powered-funklocker-ransomware/
- Tata Communications. (2025, September 30). Your weekly threat intelligence advisory. https://www.tatacommunications.com/hubfs/TaCO-2024/threat-advisory/doc/threat-intelligence-advisory-30-september-2025.pdf
- Canadian Centre for Cyber Security. (2025). Alerts and advisories (Alert AL25-012). https://www.cyber.gc.ca/en/alerts-advisories
- Australian Signals Directorate's Australian Cyber Security Centre. (2025, September 26). Multiple vulnerabilities affecting Cisco ASA 5500-X series devices. https://www.cyber.gov.au/about-us/view-all-content/alerts-and-advisories/multiple-vulnerabilities-affecting-cisco-asa-5500-x-series-devices
- Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency. (2025, October 2). CISA adds five known exploited vulnerabilities to catalog. Retrieved from web search results
- SANS Internet Storm Center. (2025, September 30). Internet Storm Center Diary 2025-09-30: "user=admin". Sometimes you don't even need to log in. https://isc.sans.edu/diary.html
- Cybersecuritynews.com. (2025, October). New SilentSync RAT delivered via typosquatted PyPI packages. https://cybersecuritynews.com/silentsync-rat-pypi/
- The Hacker News. (2025, September). First malicious MCP server found stealing emails in rogue postmark-mcp package. https://thehackernews.com/2025/09/first-malicious-mcp-server-found.html
- CISA. (2025, September 30). CISA's cooperative agreement with the Center for Internet Security (CIS) will reach its planned end on September 30, 2025. Help Net Security. https://www.helpnetsecurity.com/2025/09/30/cisa-ms-isac-funding/
- FS-ISAC. (2025, September 26). FS-ISAC urges financial sector to adopt timeline for implementing quantum computing defenses. ABA Banking Journal. https://bankingjournal.aba.com/2025/09/fs-isac-urges-financial-sector-to-adopt-timeline-for-implementing-quantum-computing-defenses/
- Arghire, I. (2025, September 29). Dutch teens arrested for allegedly helping Russian hackers. SecurityWeek. https://www.securityweek.com/dutch-teens-arrested-for-allegedly-helping-russian-hackers/
- Associated Press. (2025, September 26). Interpol says 260 suspects in online romance scams have been arrested in Africa. SecurityWeek. https://www.securityweek.com/interpol-says-260-suspects-in-online-romance-scams-have-been-arrested-in-africa/
- Cybersecuritynews.com. (2025, October). 17-year-old hacker responsible for Vegas casinos hack has been released. https://cybersecuritynews.com/alleged-casino-hacker-released/
- Check Point Research. (2025, September 29). 29th September – Threat intelligence report. https://research.checkpoint.com/2025/29th-september-threat-intelligence-report/
- Cybersecuritynews.com. (2025, October). Lotte Card data breach exposes 3 million customers. https://cybersecuritynews.com/lotte-card-data-breach/
- Cybersecuritynews.com. (2025, October). UK nursery chain ransomware attack targets 8,000 children. https://cybersecuritynews.com/uk-nursery-ransomware/
- Cybersecuritynews.com. (2025, October). Hackers attempting to exploit Grafana vulnerability that enables arbitrary file reads. https://cybersecuritynews.com/grafana-vulnerability-exploit/
- Tenable. (2025, September 10). September 2025 Patch Tuesday: Microsoft addresses 80 CVEs. https://www.tenable.com/blog/microsofts-september-2025-patch-tuesday-addresses-80-cves-cve-2025-55234


